Figure 4.
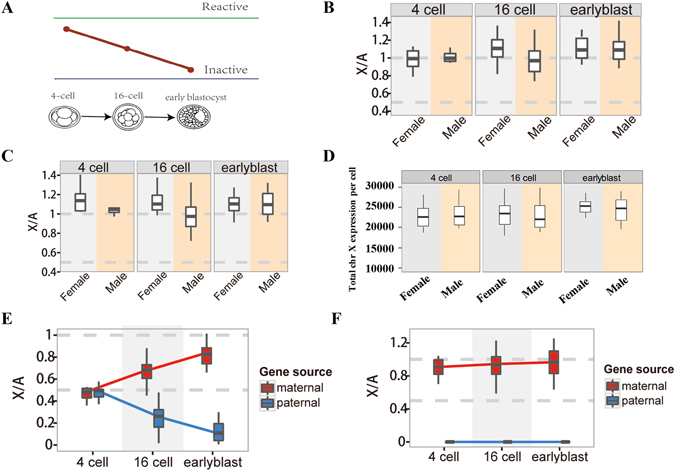
Comparisons of RNA-Seq gene expression levels between the X chromosome and autosomes in mouse early embryogenesis. (A) Schematic illustration of the process of inactivation in mouse early embryogenesis: The initiation of iXCI begins at early preimplantation in embryos and Xp-Xist is expressed around the four-cell stage. Next, the active paternal X chromosome becomes gradually inactive from the four-cell stage to early blastocyte stage to form a process from X reactivation to X inactivation. (B) X: A ratios of median expressions according to all reads for each sex and embryonic day. There were no differences between each types of embryonic cells and between males and females. (P > 0.05, by Student’s t-test). (C) X: AA ratios of median expressions according to SNP-containing reads for each sex and embryonic day. There were no differences between each types of embryonic cells and between males and females. (P > 0.05, by Student’s t-test). (D) Boxplots showing the distribution of cellular X chromosome FPKM sums for each sex and embryonic day. There were no differences between each types of embryonic cells and between males and females. (P > 0.05, by Student’s t-test). (E) Comparisons of X: AA ratios of median expressions between paternal X chromosome and maternal X chromosome from female 4-cell stage (N = 11), 16-cell stage (N = 21) and early blastocyst stage (N = 15) in female embryo. (F) Comparisons of X: AA ratios of median expressions between paternal X chromosome and maternal X chromosome from male 4-cell stage (N = 3), 16-cell stage (N = 27) and early blastocyst stage (N = 28) in male embryo. N represents the number of single cell RNA-seq data with this stage in the parentheses after early embryogenesis. The percentiles in all boxplots are 0.05, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75 and 0.95.
