Figure 1.
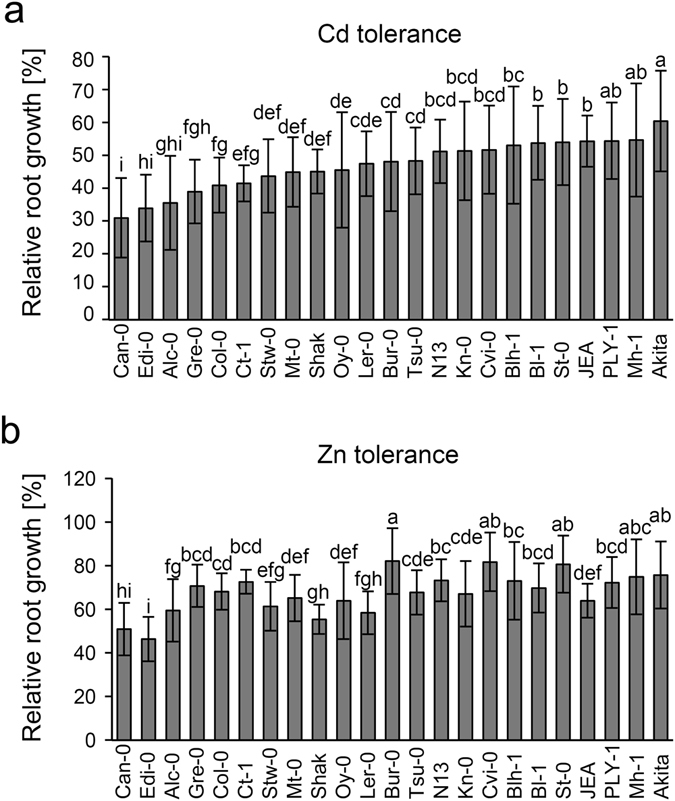
Natural variation in A. thaliana Zn and Cd tolerance. 23 accessions of the Versailles Core24 were grown on vertical agar plates under control conditions or in the presence of either 5 µM CdCl2 (a) or 50 µM ZnSO4 (b). Length of primary roots was determined after 12–14 d. Relative root growth of seedlings as an indicator for tolerance was calculated as follows: root length metal treatment/mean root length control conditions × 100. Absolute root lengths (in mm) under control conditions were: Bl-1: 64 ± 17; Stw-0:66 ± 26; N13: 69 ± 26; Akita: 70 ± 18; Shak: 77 ± 19; St-0: 82 ± 14; Blh-1: 83 ± 16; Ct-1: 84 ± 19; Kn-0: 85 ± 20; Can-0: 85 ± 16; Mh-1: 87 ± 18; Col-0: 88 ± 15; Ply-1: 90 ± 22; Cvi-0: 90 ± 14; Oy-0: 91 ± 23; Edi-0: 91 ± 16; JEA: 92 ± 22; Tsu-0: 94 ± 21; Ler-0: 94 ± 24; Mt-0: 96 ± 17; Bur-0: 99 ± 22; Gre-0: 102 ± 23; Alc-0: 103 ± 20). Data represent means ± SD. Per accession 17 to 185 plants were compared. The average n was 119. Statistical analysis was performed via one-way ANOVA and data were grouped based on Tukey’s 95% confidence intervals.
