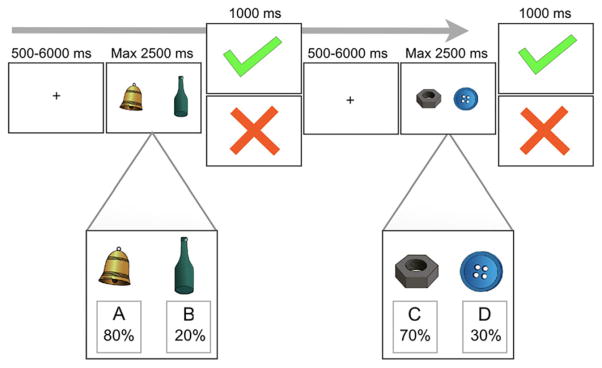
Figure 1.
The study design of our probabilistic learning task is detailed in this figure. Participants were presented with two color drawings of everyday objects and instructed to choose one of the two stimuli by pressing a button. Feedback was delivered with two different randomized probabilistic schedules (an 80/20 or 70/30 positive feedback/negative feedback schedule). In the example on the left side, the bell was rewarded on 80% of trials, while the bottle was rewarded on 20% of trials. In the other pairing, on the right side, the bolt was associated with 70% positive feedback, while the button was associated with 30% positive feedback [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]