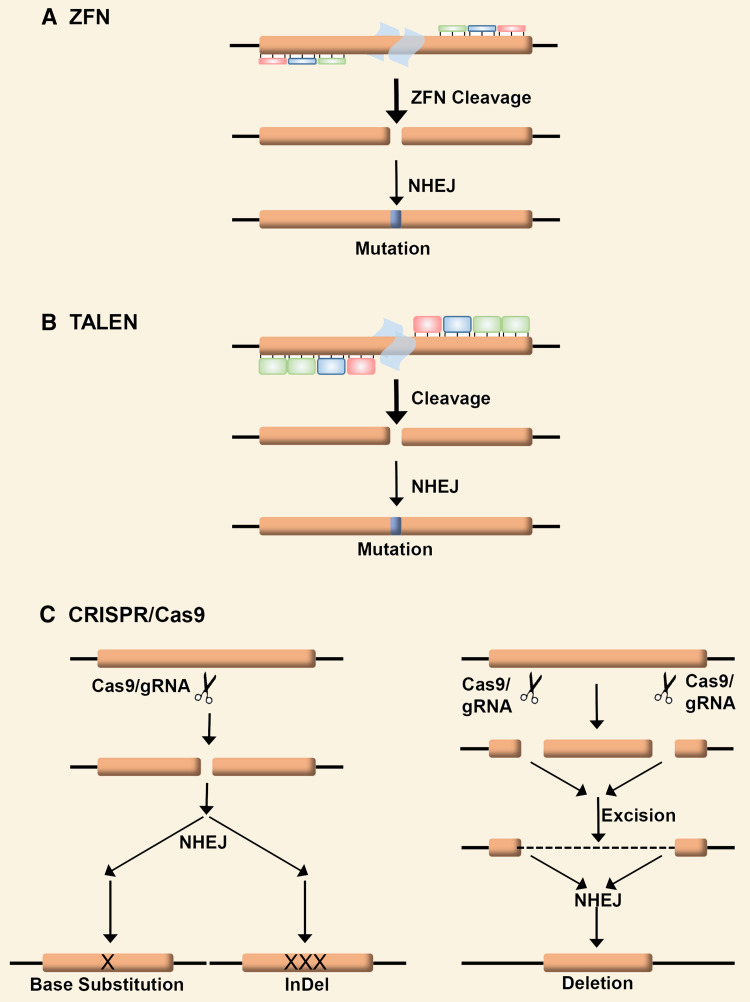
Fig. 2.
Schematic of the gene-editing technologies. a Zinc-finger nucleases (ZFN) are a class of gene-editing proteins, which are fusion proteins between the nonspecific endonuclease cleavage domain of the FokI restriction enzyme and a custom-designed Cys2-His2 zinc-finger protein, which confer specificity and give an enzyme that can make sequence-specific DNA double-strand breaks. b Transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALEN) are another class of reagents also based on FokI fusion proteins and have a targeting domain that is taken from the Xanthomonas bacteria TAL effector proteins. MEG (MegaTAL) are derived from the homing endonucleases known as the meganucleases fused with the TAL effector proteins. c Clustered regulatory interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)-associated 9 (Cas9) is a two-component system consisting of a single-guide RNA (gRNA) that, when expressed with the Cas9 endonuclease enzyme, is able to find and cut a DNA target specified by the sequence of the guide RNA