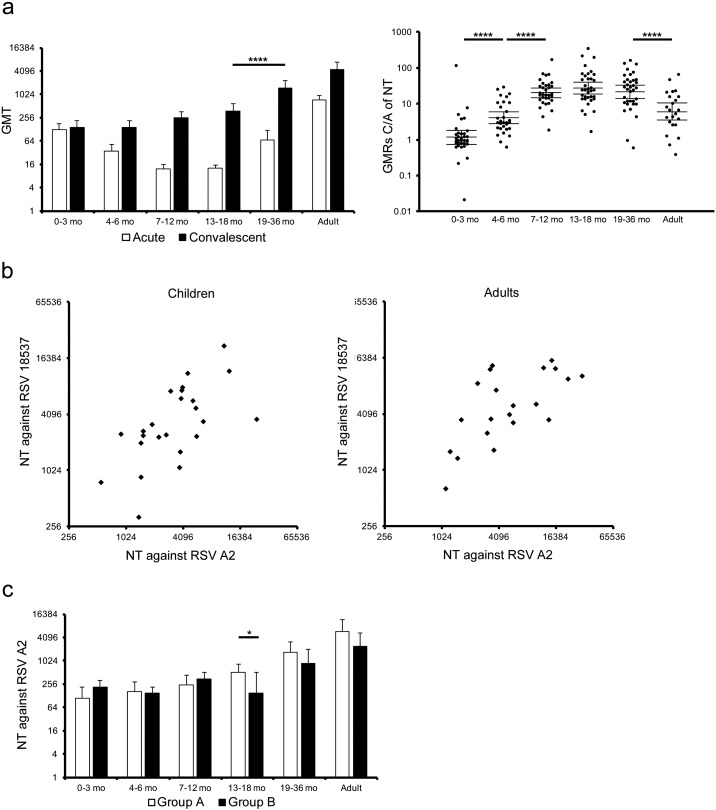
Fig. 1.
Serum neutralization activity upon natural RSV infection.
(a) Sera were subjected to a microneutralization assay to determine neutralization titers against RSV A2 strain. A left panel represented neutralization titer in acute phase or convalescent phase, and a right panel did the GMRs C/A of NT. The mean ± 95% CI was estimated by linear model, and was shown in the graphs. Neutralization titer in acute phase: 0–3 mo, n = 34; 4–6 mo, n = 30; 7–12 mo, n = 33; 13–18 mo, n = 35; 19–36 mo, n = 35; adults, n = 23. Neutralization titer in convalescent phase: 0–3 mo, n = 35; 4–6 mo, n = 30; 7–12 mo, n = 34; 13–18 mo, n = 35; 19–36 mo, n = 35; adults, n = 23. GMRs C/A of NT: 0–3 mo, n = 34; 4–6 mo, n = 30; 7–12 mo, n = 33; 13–18 mo, n = 35; 19–36 mo, n = 35; adults, n = 23. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001. (b) Sera, which showed high neutralization activity against RSV A2 in panel (a), were subjected to a microneutralization assay to evaluate NT against RSV 18537 strain. Children: r = 0.705, p < 0.0001 (n = 24), adults: r = 0.657, p = 0.0012 (n = 21). (c) Neutralization titers were also analyzed in two distinct groups according to RSV groups infected during the research period to evaluate the cross neutralization activity at convalescent phase. Group A: 0–3 mo, n = 20; 4–6 mo, n = 16; 7–12 mo, n = 17; 13–18 mo, n = 25; 19–36 mo, n = 21; adults, n = 12. Group B: 0–3 mo, n = 14; 4–6 mo, n = 11; 7–12 mo, n = 13; 13–18 mo, n = 6; 19–36 mo, n = 8; adults, n = 5. The mean ± 95% CI was estimated by the linear model, and were shown in the graphs. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001.