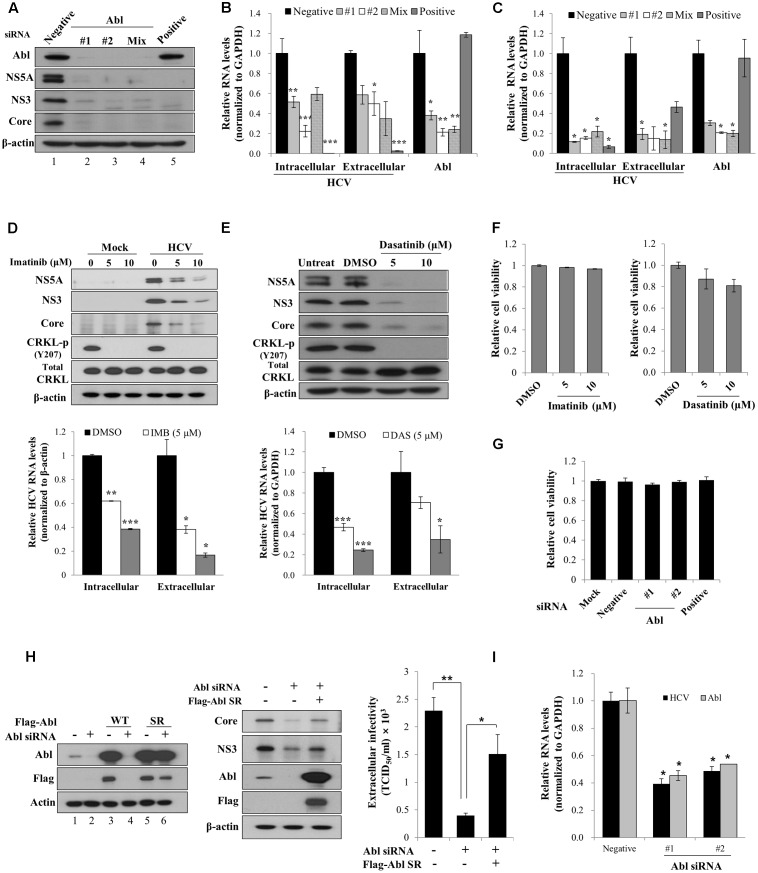
FIGURE 1.
Abl is required for HCV propagation. (A) Huh7.5 cells were transfected with 10 nM concentration of the indicated siRNAs. At 48 h after transfection, cells were then infected with Jc1 for 4 h using an MOI of 0.5. Total cell lysates harvested at 48 h post-infection were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Negative denotes universal negative control siRNA. Positive indicates HCV-specific siRNA targeting the 5′ NTR of Jc1. (B) Huh7.5 cells were treated as described in (A) and then RNA levels of both HCV and Abl were quantified by qRT-PCR. Experiments were carried out in triplicate. The asterisks indicate significant differences (∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001). Error bars indicate the standard deviations of the means. (C) Huh7.5 cells were transfected with 10 nM concentration of the indicated siRNAs. At 48 h after transfection, cells were then infected with H77D for 4 h. At 48 h post-infection, RNA levels of both HCV and Abl were analyzed by qRT-PCR. (D) (Upper panel) Huh7.5 cells pretreated with imatinib were either mock-infected or infected with Jc1 for 4 h. Cells were further incubated with either DMSO (vehicle) or two different doses of imatinib for 48 h. Total cell lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (Lower panel) Both intracellular and extracellular HCV RNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR. (E) (Upper panel) Huh7.5 cells were pretreated with either DMSO or two different doses of dasatinib and then infected with Jc1 for 4 h. Cells were further incubated with either DMSO or dasatinib for 48 h. Total cell lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (Lower panel) Both intracellular and extracellular HCV RNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR. Experiments were performed in triplicate. The asterisks indicate significant differences (∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001). (F) Huh7.5 cells were treated with either DMSO or two different doses of imatinib (left panel) or dasatinib (right panel). Forty-eight hours after inhibitor treatment, cell viability was determined by a WST assay. (G) Huh7.5 cells were transfected with 20 nM of the indicated siRNAs. At 72 h after transfection, cell viability was determined by a WST assay. (H) (Left panel) Huh7.5 cells were transfected with p3XFlag-Abl wild-type (WT) or p3XFlag-Abl siRNA-resistant (SR) expression plasmid. At 24 h after transfection, total cell lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (Middle panel) Huh7.5 cells were transfected with either negative siRNA or Abl-specific siRNA. At 24 h transfection, cells were further transfected with Flag-tagged Abl SR plasmid for 24 h and then infected with Jc1 for 4 h. Cell lysates harvested at 2 days post-infection were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (Right panel) Naïve Huh7.5 cells were inoculated with the supernatant harvested from experiment described in the middle panel. At 2 days post-infection, cells were fixed with methanol and HCV infectivity was determined by TCID50 assay. (I) Primary human hepatocytes were transfected with negative siRNA or Abl-specific siRNAs. At 2 days after transfection, cells were infected with Jc1 for 4 h. Cells were harvested at 2 days post-infection and then intracellular RNA levels of HCV and Abl were determined by qRT-PCR.