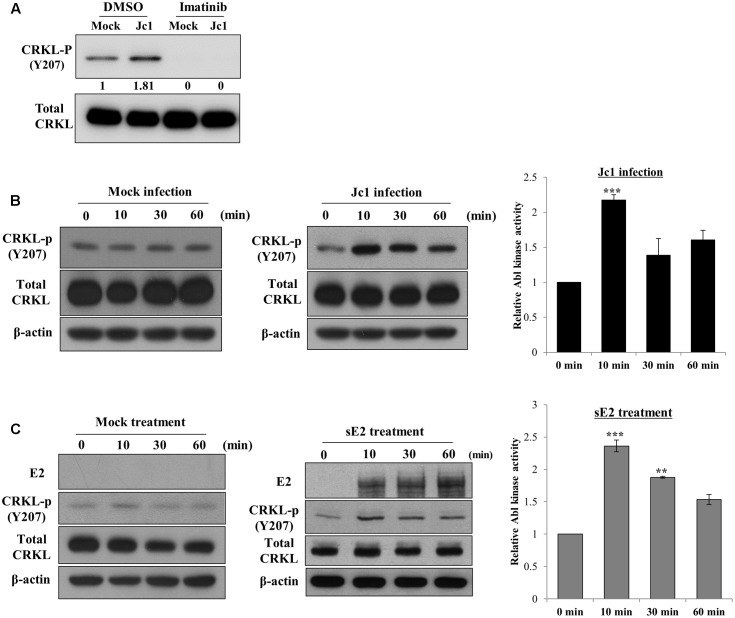
FIGURE 4.
Hepatitis C virus infection activates Abl kinase. (A) Huh7.5 cells were serum-starved for 16 h and then treated with either DMSO (vehicle) or 10 μM of imatinib for 2 h. Cells were either mock-infected or infected with Jc1 using an MOI of 5. At 10 min post-infection, total cell lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (B) Huh7.5 cells were serum-starved for 16 h and then either mock-infected (left panel) or infected with Jc1 (middle panel). At the indicated time points, total cell lysates were immunoblotted. (Right panel) Abl kinase activities were determined by measuring band intensities of CRKL-p/total CRKL using ImageJ and shown as relative fold from the mock control. (C) Huh7.5 cells were serum-starved for 16 h and then either mock-treated (left panel) or treated with 10 μg sE2 derived from H77 (middle panel). Total cell lysates harvested at each time points were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (Right panel) Abl kinase activities were determined by measuring band intensities of CRKL-p/total CRKL using ImageJ and shown as relative fold from the mock control. sE2, soluble HCV E2 protein. The asterisks indicate significant differences (∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001).