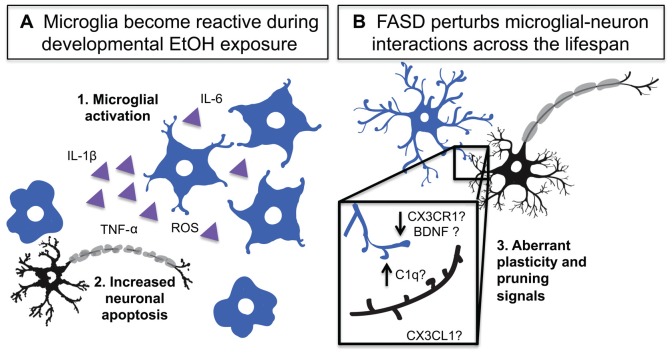
Figure 2.
Developmental EtOH exposure activates microglia and impairs their homeostatic functions. (A) Developmental EtOH exposure causes acute microglial activation which produces: 1. Activation and production of inflammatory signals 2. Increased neuronal death and phagocytosis. (B) Developmental EtOH exposure produces changes in dendritic spine density and could impact microglial interactions with synapses. 3. A number of microglia-neuron signaling systems could be disrupted and contribute to spine density changes including: complement dependent pruning, decreased CX3CR1 signaling altered BDNF release.