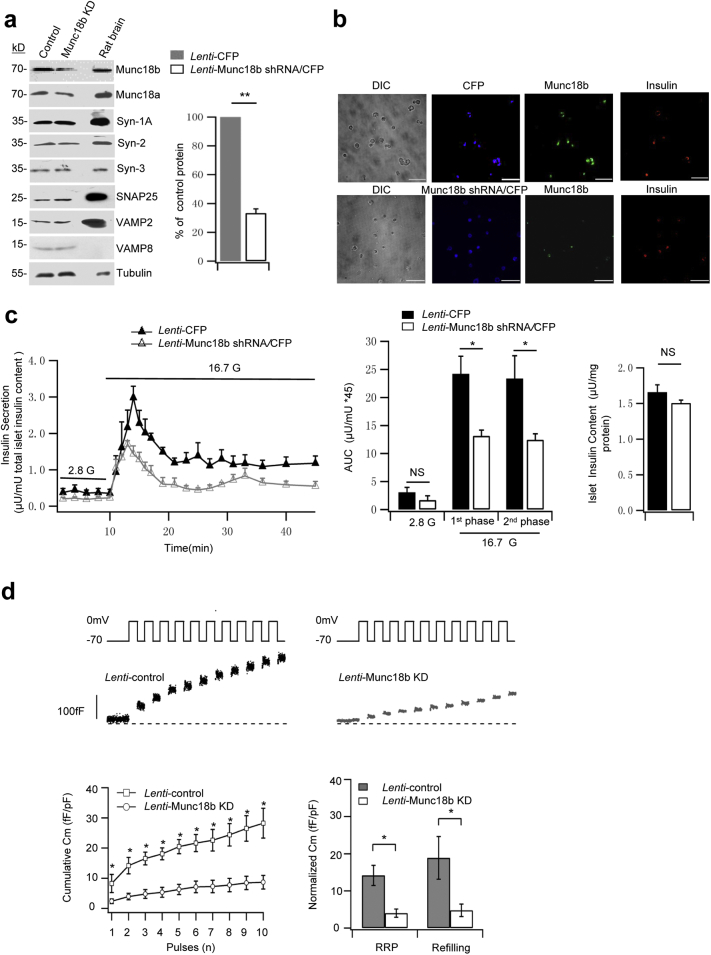
Fig. 2.
Munc18b depletion decreases biphasic GSIS in human islets.
(a) Western blot analysis of Lenti-Munc18b shRNA/CFP-induced knockdown of Munc18b expression on normal human islets; representative of 3 experiments. Right: Densitometric analysis of the reduction of Munc18b normalized to percentage of control (N = 3); there was no change in any of the other proteins after Munc18b KD, therefore analysis not shown.
(b) Islets transduced with Lenti-Munc18b shRNA/CFP (bottom) or Lenti-CFP (top) were dispersed to single cells, then triple labeled with CFP (assigned blue color), Munc18b/Cy5 (assigned green color) and insulin/TxRed (red color). Scale bar: 100 μm.
(c) Islet perifusion assays on Lenti-Munc18b shRNA/CFP- vs Lenti-CFP-transduced normal human islets; corresponding AUCs analysis of first- (10–25 min) and second-phase (25–45 min) GSIS (middle) and total islet insulin content (right). N = 4 human islet donors.
(d) Cm recording performed on single human β-cells (CFP-positive) infected with Lenti-Munc18b shRNA/CFP (N = 8) or Lenti-CFP (N = 6). Top: Representative recordings of ΔCm. Bottom left: Cumulative changes in Cm normalized to basal cell Cm (fF/pF). Bottom right: Summary of RRP (ΔCm1st–2nd pulses) and rate of SG refilling (ΔCm3rd–10th pulses).
Data are shown as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, NS: no significant difference.