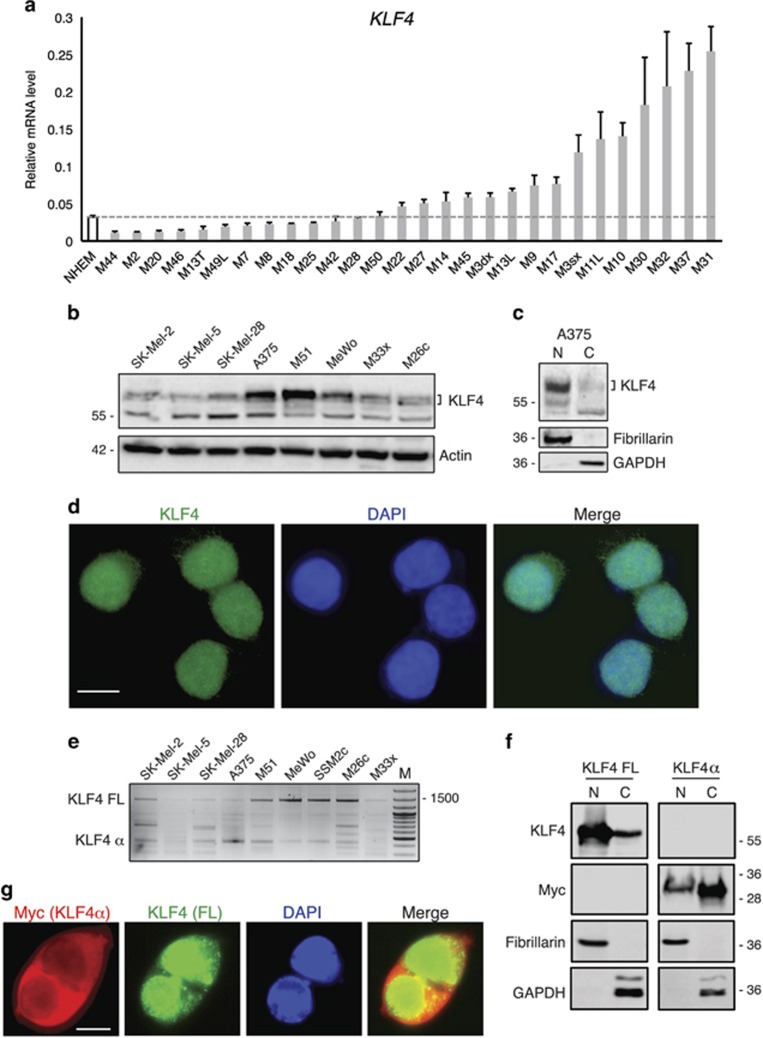
Figure 1.
KLF4 expression in human melanoma. (a) qPCR analysis of full length KLF4 in a panel of 28 human melanomas and normal human epidermal melanocytes (NHEM). The y axis represents expression ratio of gene/(GAPDH and β-ACTIN average). (b) Western blotting analysis of KLF4 protein in a panel of three patients derived melanoma cells (M51, M26c and M33x) and five commercial cell lines (A375, SK-Mel2, SK-Mel 5, SK-Mel28 and Mewo). Actin was used as loading control. (c) Subcellular localization of endogenous KLF4 in A375 melanoma cells. Cell fractionation was performed and lysates were subjected to western blotting with anti-KLF4, anti-GAPDH (control for cytoplasmic proteins) and anti-Fibrillarin (control for nuclear proteins) antibodies. (d) Representative images of A375 cells after immuno-labeling with anti-KLF4 antibody analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Nuclei were counterstained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (e) PCR analysis in a panel of four patients derived melanoma cells and five commercial cell lines showing two major KLF4 splicing variants: KLF4 full length (KLF4 FL, 1470 bp) and KLF4α (500 bp). (f) Subcellular localization of transiently transfected KLF4 FL and Myc-tagged KLF4α in M26c melanoma cells. Cell fractionation was performed 48 h after transfection and lysates were subjected to western blotting with anti-KLF4 (for KLF4 FL), anti-Myc (for Myc-KLF4α), anti-GAPDH (control for cytoplasmic proteins) and anti-Fibrillarin (control for nuclear proteins) antibodies. (g) Representative images of KLF4α and KLF4 FL subcellular localization after transient transfection of Myc-tagged KLF4α and KLF4 FL in M26c cells. Immunolocalization was with anti-Myc antibody for Myc-tagged KLF4α (red) and anti-KLF4 for KLF4 FL (green). Nuclei were counterstained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. Scale bar=10 μm.