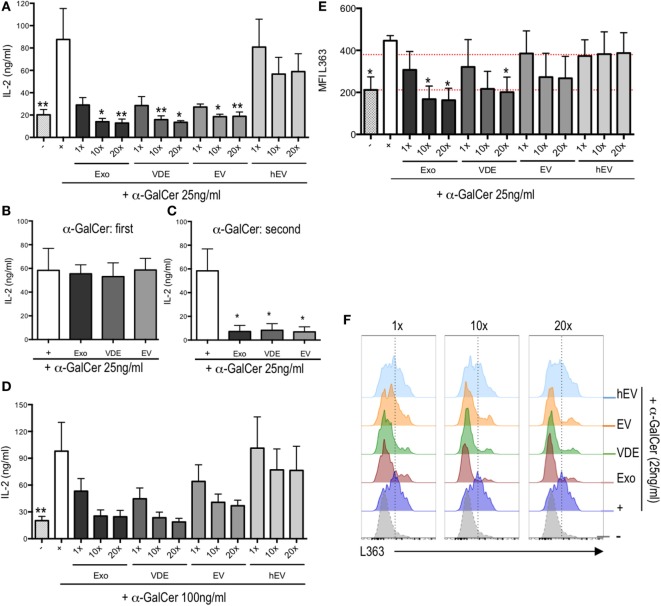
Figure 3.
Leishmania infantum Exo, extracellular vesicle (EV), and vesicle-depleted-exoproduct (VDE) inhibited invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cell activation by plate-bound α-GalCer/CD1d complexes in a dose-dependent manner. Plate-bound mouse CD1d was loaded with a mixture of α-GalCer 25 ng/ml (A,E,F) and 100 ng/ml (D) alone (+) or in the presence of L. infantum Exo, EV, VDE, or hEV at different doses. (B) Plate-bound mouse CD1d was loaded first with α-GalCer at 25 ng/ml. Eight hours later, L. infantum Exo, EV, VDE, or hEV (20×) was added. (C) Plate-bound mouse CD1d was loaded with L. infantum Exo, EV, VDE, or hEV (20×). Eight hours later, 25 ng/ml of α-GalCer was added (second). After extensive washings, the 24.8 iNKT cell hybridoma was added and supernatants were recovered 20 h later. Data are expressed as means ± SEM of IL-2 levels detected in culture supernatants. Data are representative of two independent experiments (n = 4). All groups were tested versus positive α-GalCer (+) control group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (E) Histograms indicating MFI of L363 staining showing CD1d:α-GalCer complexes expressed by bone marrow-derived dendritic cells unstimulated (−) or previously incubated with α-GalCer (+) or α-GalCer plus L. infantum Exo, EV, VDE, or hEV at distinct doses. Data are expressed as means ± SEM from three independent experiments. (F) Representative FACS profile showing the expression of L363 as described in (E). Data are representative of three independent experiments.