Figure 1.
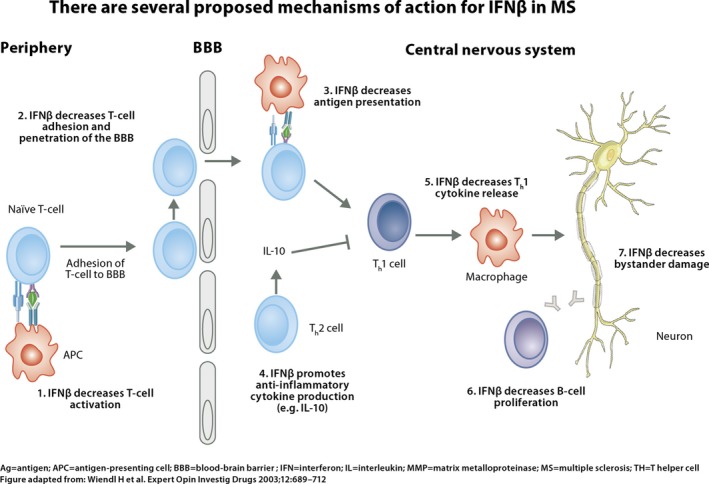
Mechanisms of action for IFNβ in multiple sclerosis. Interferon beta exerts its biological effects by binding to specific receptors on the surface of human cells. This binding initiates a complex cascade of intracellular events that leads to the expression of numerous interferon‐induced gene products and markers (Wiendl & Kieseier, 2003)
