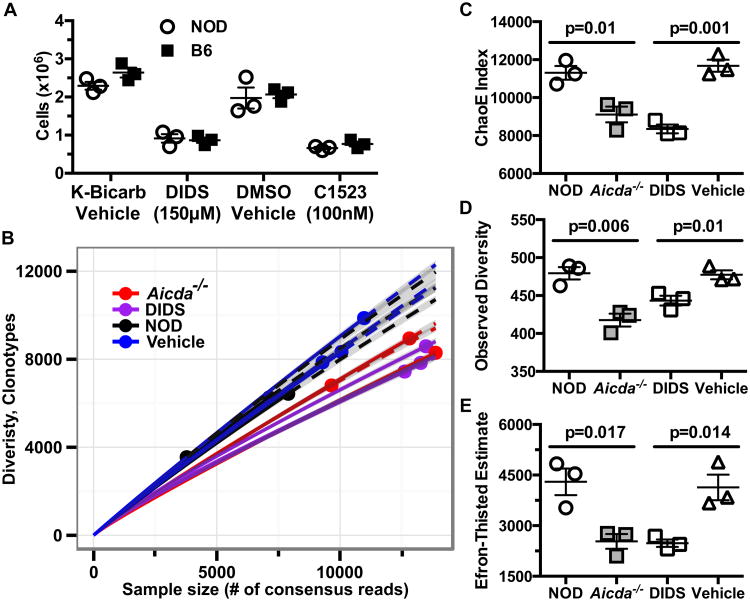
Figure 6. DIDS diminishes in vitro expansion and Ig usage diversity of NOD B-lymphocytes.
(A) Cellular yields of purified B-lymphocytes from B6 or NOD (n=3 biological replicates per group) mice cultured for 96 hours at 1×106 cells/mL with anti-CD40 (1 μg/mL) and murine IL-4 (25 ng/mL) in the presence of vehicle, 150μM DIDS, or 100nM C1523. Data are representative of one of three experiments. (B) 136,000-400,000 purified PLN B-lymphocytes from the indicated NOD experimental groups were sequenced for IgH gene usage diversity (n=3 mice per group) in one experiment. Sequences with early stop codons or frameshift mutations were filtered to display only “functional” clones. Data are presented in a rarefraction plot showing clonal diversity as a function of unique cDNA molecules sequenced. Solid and dashed lines are interpolated and extrapolated regions respectively with points marking the exact sample size and observed diversity. The shaded area represents 95% confidence interval. (C) ChaoE Index. (D) Observed diversity and (E) Efron-Thisted Estimate after 500 iterations of down sampling to 500 reads. P-values in (C-E) were calculated using Student's t-test. Scatter plots show Mean±SEM.