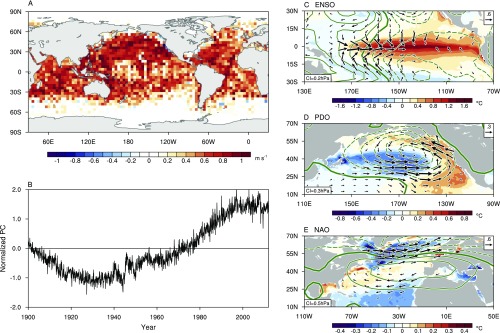
Fig. S9.
Reconstruction of SLP and marine surface wind anomalies used in the present study. (A) Spatial pattern (regressed anomaly in meters per second) and (B) principal components of the first EOF mode for uncorrected monthly mean scalar wind anomalies for 1900–2014. The first EOF mode accounts for 18.4% of the total variance. To reduce the time-varying biases, the scalar wind anomalies associated with the first EOF mode have been removed from the uncorrected data. (C–E) Regressed anomalies of SLP (contours; in hectopascals), bias-corrected marine surface wind (vectors; in meters per second), and SST (shading; in degrees Celsius) onto (C) the November–February Niño-3.4, (D) the November–March Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO), and (E) the December–March North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) indices. The Niño-3.4 index is defined as SST anomaly averaged in the central equatorial Pacific (170°–120°W, 5°S–5°N). The PDO index is defined as the principal component of the first EOF mode for the North Pacific SST anomalies (120°E–100°W, 20°–60°N), whereas the NAO index is defined as the first EOF mode for the North Atlantic SLP anomalies (90°W–40°E, 20°–80°N). For the PDO and NAO indices, the 5-y running average is applied for detrended seasonal mean data. The contour interval for SLP anomalies is indicated at the Bottom Left of each panel, with positive (negative) contours solid (dashed), and zero contours thickened.