Figure 2. Primary structure of truncated and chimeric terpenoid synthases.
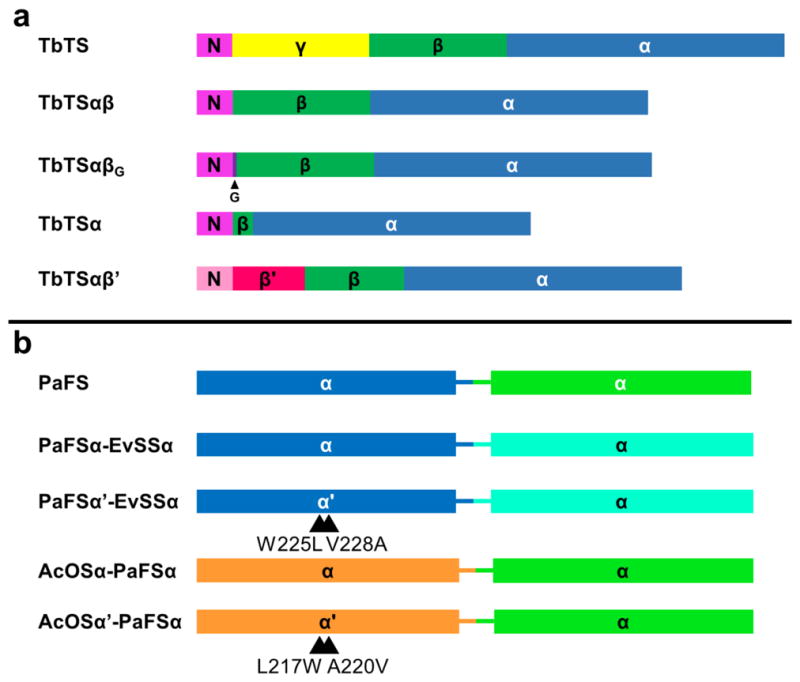
(a) For the class I diterpene synthase taxadiene synthase (TbTS), four engineered domain constructs successively downsized the αβγ domain architecture, color-coded as follows: α domain, blue; β domain, green; γ domain, yellow; N-terminal segment, magenta. The location of the single inserted glycine residue (G) in TbTSαβG is indicated by an arrow. The TbTSαβ′ is a chimera containing the N-terminal segment (pink) and part of the β domain (β′, red) of isoprene synthase. (b) Engineered bifunctional class I diterpene and sesterterpene synthases with αα domain architecture are color-coded as follows: dark blue, cyclization α domain of fusicoccadiene synthase (PaFS); orange, cyclization α domain of ophiobolin F synthase (AcOS); aquamarine, GFPP synthase α domain of stellatatriene synthase (EvSS); green, GGPP synthase α domain of fusicoccadiene synthase (PaFS).
