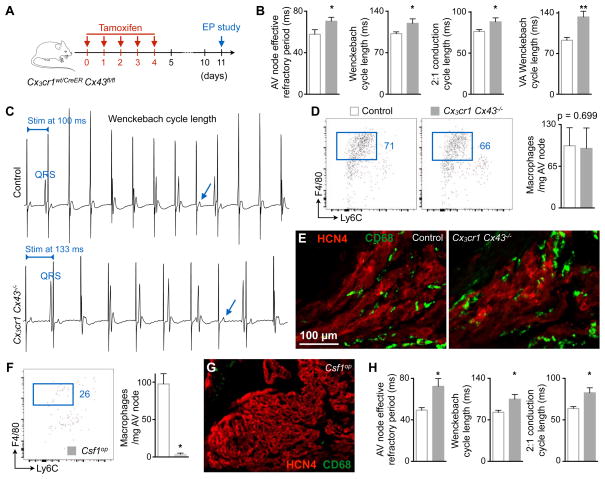
Figure 6. Cx43 Deletion in Macrophages and Congenital Lack of Macrophages Delay AV Conduction.
(A) Experimental outline of the electrophysiological (EP) study performed on mice lacking Cx43 in macrophages.
(B) AV node effective refractory period at 120 ms pacing frequency, and pacing cycle lengths at which Wenckebach conduction, 2:1 conduction and ventriculo-atrial (VA) Wenckebach conduction occurred in control (n = 5 to 9) and Cx3cr1 Cx43−/− (n = 6 to 8) mice. Data are mean ± SEM, 2 independent experiments, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01, Student’s t test and nonparametric Mann-Whitney test.
(C) Surface ECG from control and Cx3cr1 Cx43−/− mice illustrating the Wenckebach cycle length. Arrows indicate missing QRS complexes. Stim, stimulation.
(D) Flow cytometric quantification of AV node macrophages in control and Cx3cr1 Cx43−/− mice. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 6 mice per group, nonparametric Mann-Whitney test.
(E) Immunofluorescence images of control and Cx3cr1 Cx43−/− AV node stained for CD68 (green) and HCN4 (red).
(F) Quantification of AV node macrophages in control (n = 5) and Csf1op (n = 4) mice by flow cytometry. Data are mean ± SEM, 3 independent experiments, *p < 0.05, nonparametric Mann-Whitney test.
(G) Immunofluorescence image of a Csf1op AV node stained for CD68 (green) and HCN4 (red).
(H) AV node effective refractory period at 120 ms pacing frequency, and pacing cycle lengths at which Wenckebach and 2:1 conduction occurred in control (n = 8) and Csf1op (n = 7) mice. Data are mean ± SEM, 4 independent experiments, *p < 0.05, nonparametric Mann-Whitney test.