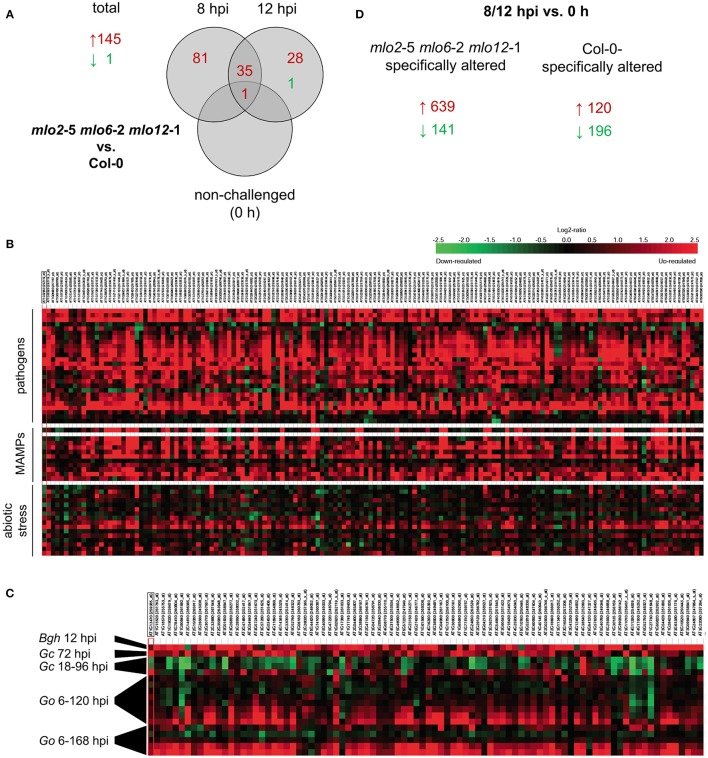
Figure 2.
mlo2 mlo6 mlo12 contributes to accelerated transcript accumulation of (defense) related genes during G. orontii infection. Four to five-week-old mlo2-5 mlo6-2 mlo12-1 and Col-0 plants were inoculated with G. orontii and sampled prior to inoculation (0 h, non-challenged) or at 8 and 12 hpi for comparative transcriptome analysis using the Affymetrix ATH1 GeneChip. All samples were analyzed in triplicate. (A) Total numbers of genes and Venn diagram displaying the number of genes with statistically significantly (P ≤ 0.05) increased (≥ 2-fold; red) or decreased (≤ 0.5-fold; green) transcript abundance in mlo2 mlo6 mlo12 vs. Col-0 plants at the indicated time points after G. orontii challenge. (B) Heat map of relative expression of genes that were statistically significantly induced (≥ 2-fold; P ≤ 0.05) in mlo2 mlo6 mlo12 vs. Col-0 in selected Genevestigator studies based on the displayed stimuli. (C) Heat map of relative expression of genes associated with defense-related GO terms that were statistically significantly induced (≥ 2-fold; P ≤ 0.05) in mlo2 mlo6 mlo12 vs. Col-0 in powdery mildew-related Genevestigator studies (Bgh, B. graminis f.sp. hordei; Go, G. orontii (6, 12, 18, 24, 48, 72, 96, 120 hpi and 6, 24, 72, 120, 168 hpi); Gc, G. cichoracearum (18, 36, 96 hpi). (D) Number of genes with statistically significantly altered (≥ 2-fold (red) or ≤ 0.5-fold (green); P ≤ 0.05 P ≤ 0.05) transcript abundance in mlo2 mlo6 mlo12 or Col-0 at 8 and/or 12 hpi vs. 0 h.