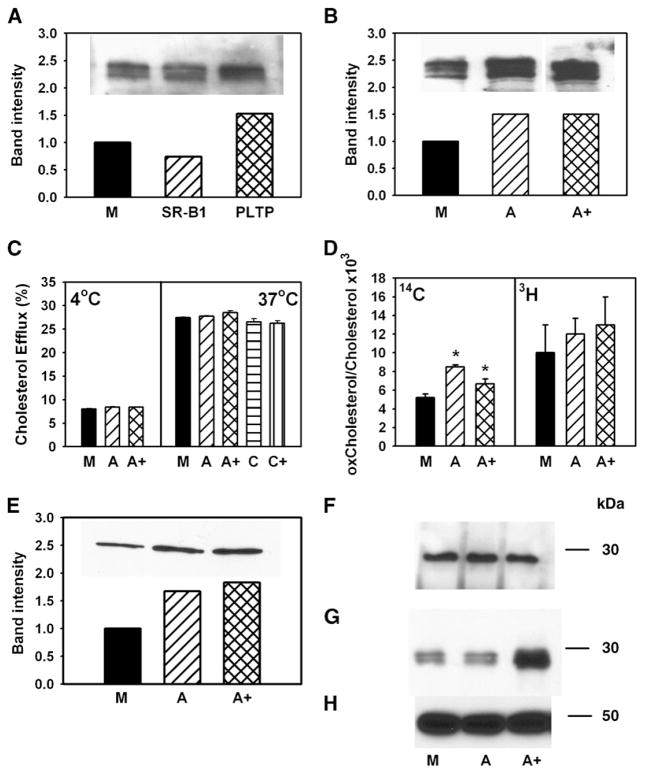
Fig. 8.
Possible mechanisms of stimulation of cholesterol efflux. A, B: RAW 264.7 cells were transiently transfected with mock (M), SR-BI, PLTP, ABCA1 (A), or ABCA1 + SR-BI + PLTP+ CYP27A1 (A+). The abundance of ABCA1 in cells was assessed by Western blotting. C: RAW 264.7 cells were transiently transfected with mock (M), ABCA1 (A), ABCA1 + SR-BI + PLTP+ CYP27A1 (A+), caveolin-1 (C), or caveolin-1 + SR-BI (C+). Cells were labeled with [3H]cholesterol, and cholesterol efflux to methyl-β-cyclodextrin (final concentration 5 mM) at 4°C (left) or 37°C (right) was assessed as described in Materials and Methods. Cholesterol efflux was expressed as a proportion of [3H]cholesterol transferred from cells to medium. Means ± SEM of quadruplicate determinations are shown. D: RAW 264.7 cells were transiently transfected with mock (M), ABCA1 (A), or ABCA1 + SR-BI + PLTP + CYP27A1 (A+). Cells were labeled with [14C]cholesterol for 48 h at 37°C, washed, and labeled with [3H]acetate for 3 h at 15°C. Cells were then warmed to 37°C for 20 min, cooled to 4°C, washed, and treated with cholesterol oxidase (final concentration 1 U/ml) for 3 h at 4°C. Cellular lipids were isolated and separated on TLC as described in Materials and Methods. The ratio of oxidized cholesterol to cholesterol is shown. * P < 0.01 (versus mock-transfected cells). E: RAW 264.7 cells were transiently transfected with mock (M), ABCA1 (A), or ABCA1 + SR-BI + PLTP+ CYP27A1 (A+). The abundance of ABCA1 on cell surface was assessed as accessibility of ABCA1 to biotinilation as described in Materials and Methods. F, G: RAW 264.7 cells were transiently transfected with mock (M), ABCA1 (A), or ABCA1 + SR-BI + PLTP+ CYP27A1 (A+). ApoA-I was added to the final concentration of 50 μg/ml, incubated for 1 h at 37°C, and washed out. Dithiobis(succinimidyl)propionate was added to the final concentration of 250 μM and incubated for 1 h at room temperature. Cells were then lysed, and ABCA1 was immunoprecipitated with polyclonal anti-ABCA1 antibodies. Precipitated (F) and unbound (G) fractions were diluted with loading buffer containing 5% 2-mercaptoethanol, boiled for 5 min, and subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blot using monoclonal antibody against apoA-I (F, G) or β-actin (H).