Figure 1.
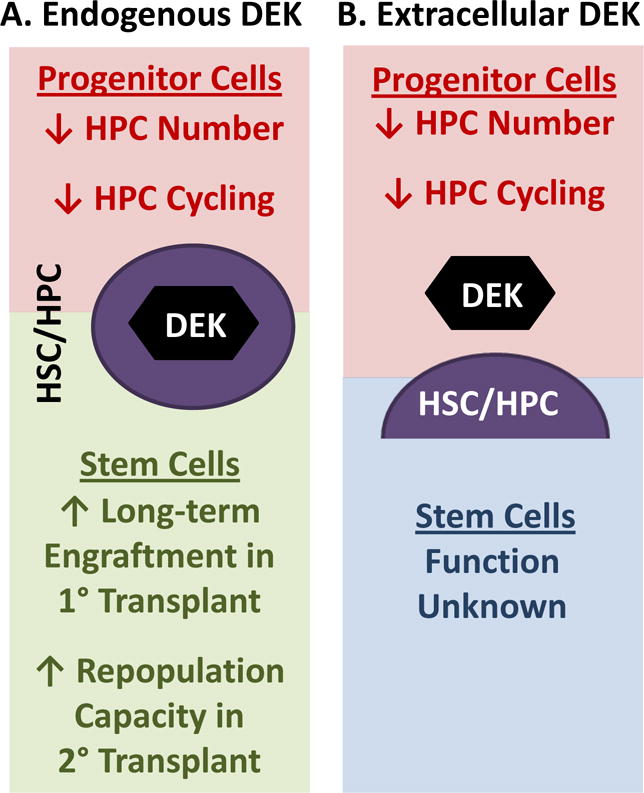
Effects of endogenous/intracellular and extracellular DEK on hematopoiesis. (A) Endogenous/intracellular DEK decreases hematopoietic progenitor cell (HPC) numbers and inhibits HPC cycling while increasing the long-term competitive repopulation capacity in lethally irradiated congenic mice and increasing the repopulation of lethally-irradiated secondary mouse recipients in a non-competitive transplantation model indicating that endogenous DEK enhances hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) repopulating and/or self-renewal capability. (B) Extracellular DEK, as determine through the co-culture of either mouse bone marrow cells and/or low-density human cord blood cells with recombinant DEK, decreases HPC numbers and inhibits HPC cycling. The effect of extracellular DEK on HSC function is currently unknown.
