Figure 2. Rh7 contributes to light sensitivity of circadian pacemaker neurons.
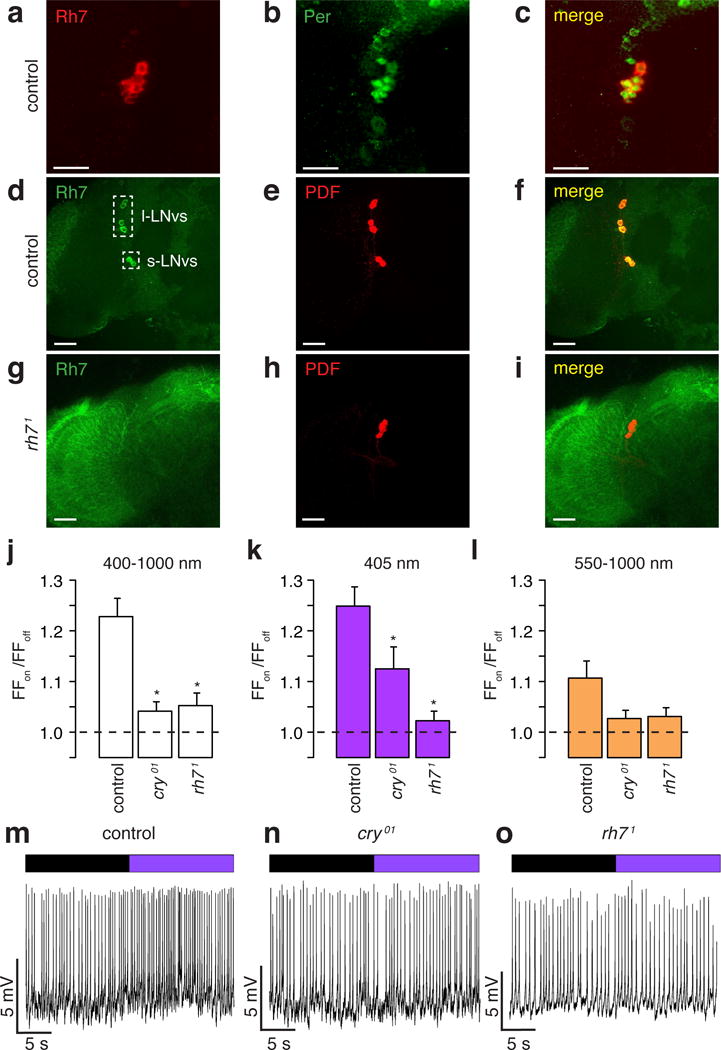
a–i, Control and rh71 brains stained with the indicated antibodies Merged images are to the right. Scale bars indicate 20 μm. j–l, Average firing frequencies of l-LNvs during “lights on” relative to the firing frequencies during “lights off” (FFon/FFoff). * Significant differences from the control (p<0.05). j, White light. Control (n =74), cry01 (n =80, p<0.05 vs. control) and rh71 (n =60, p<0.05 vs. control). k, 405 nm violet light. Control (n=76), cry01 (n=89, p<0.05 vs. control) and rh71 (n=66, p<0.05 vs. control). l, Orange light. Control (n=58), cry01 (n=65), and rh71 (n=46). m–o, Representative recordings showing responses of l-LNv neurons to 405 nm light. Purple bar=405 nm light; black bar= no light.
