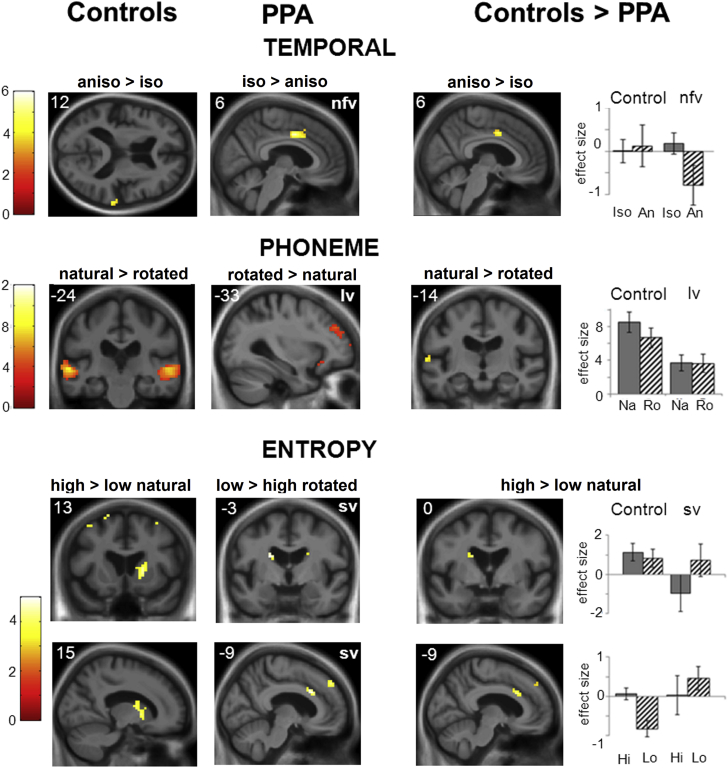
Fig. 2.
Statistical parametric maps showing fMRI associations of speech signal processing across participant groups. Significant regional brain activations for contrast of interest are shown within healthy control and particular patient groups (left and middle image panels; T scores for relevant contrasts coded in color bars) and between groups (significantly greater activation in healthy controls than the corresponding patient group; right image panels); additional maps showing all significant contrasts are presented in Fig. S3 on-line. Contrasts are coded as follows (see text for details): temporal, anisochronous > isochronous conditions (within-controls; controls > nfvPPA), isochronous > anisochronous conditions (within-nfvPPA); phoneme, natural > spectrally rotated speech conditions (within-controls; controls > lvPPA), spectrally rotated > natural speech conditions (within-lvPPA); entropy, high > low sequence entropy conditions (for natural speech conditions, within-controls; controls > svPPA), low > high sequence entropy conditions (for spectrally rotated speech conditions, within-svPPA). Maps are rendered on representative sections of the study-specific group mean T1-weighted structural MR image in MNI space; the plane of each section is indicated using MNI coordinates and the left cerebral hemisphere is displayed on the left in axial and coronal sections. Maps have been thresholded at p < 0.001 uncorrected over the whole brain for display purposes; all activations shown were significant at p < 0.05 after family-wise error correction for multiple comparisons (see Table 2). Plots of condition effect size (mean beta parameter estimate ± standard error) are shown (right) for the group comparisons, based on data for peak voxels from the between-group contrasts (see Table 2) in anterior cingulate (temporal contrast), posterior superior temporal gyrus (phoneme contrast), caudate nucleus (entropy contrast, top), and anterior cingulate (entropy contrast, bottom). Abbreviations: An/aniso, anisochronous; Hi, high entropy; Iso, isochronous; Lo, low entropy; lvPPA, logopenic variant primary progressive aphasia; Na/natural, natural speech; nfvPPA, nonfluent variant primary progressive aphasia; Ro/rotated, rotated speech; svPPA, semantic variant primary progressive aphasia. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)