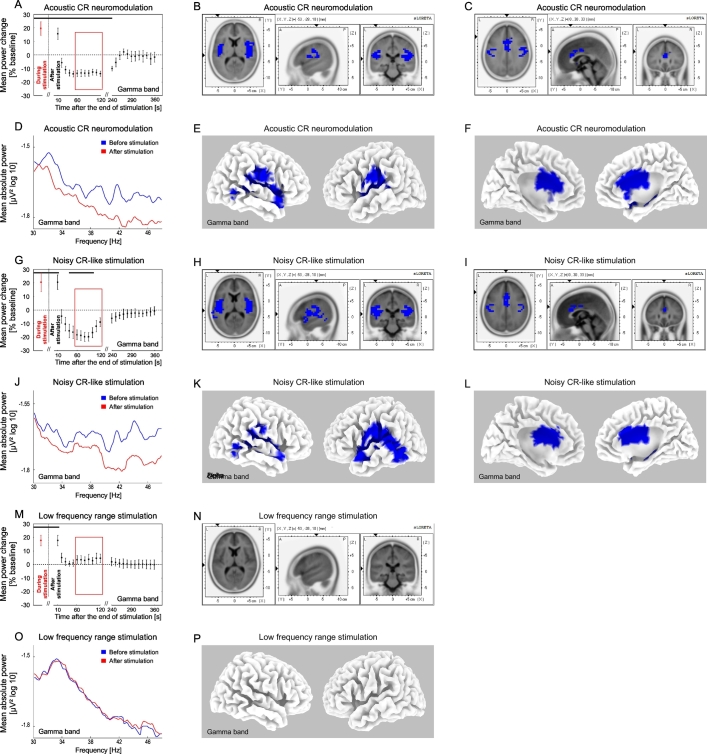
Fig. 6.
Changes of the gamma power after the end of acoustic stimulation. Time course of the mean gamma (30–48 Hz) power of the auditory BESA source activity during (averaged over the whole stimulation period, red) and after the end (black) of acoustic CR neuromodulation (A), the noisy CR-like stimulation (G) and the LFR stimulation (M) expressed as a percentage change from the baseline activity. Significant changes are marked with the horizontal black line (A, G, M). Format as in Fig. 4. Power spectra for the gamma frequency range at baseline and for the time period 60–120 s (inside the red window in A, G, M) after end of the acoustic CR neuromodulation (D), the noisy CR-like stimulation (J) and the LFR stimulation (O). The effect of acoustic CR neuromodulation (B, C, E, F), noisy CR-like stimulation (H, I, K, L) and the LFR stimulation (N, P) on the mean current source density analyzed by sLORETA (format as in Fig. 4). The strongest decrease compared to baseline (indicated by blue voxels) was localized in the left and right superior temporal gyrus after the noisy CR-like stimulation (xyz 37, − 28, 9; BA 41).