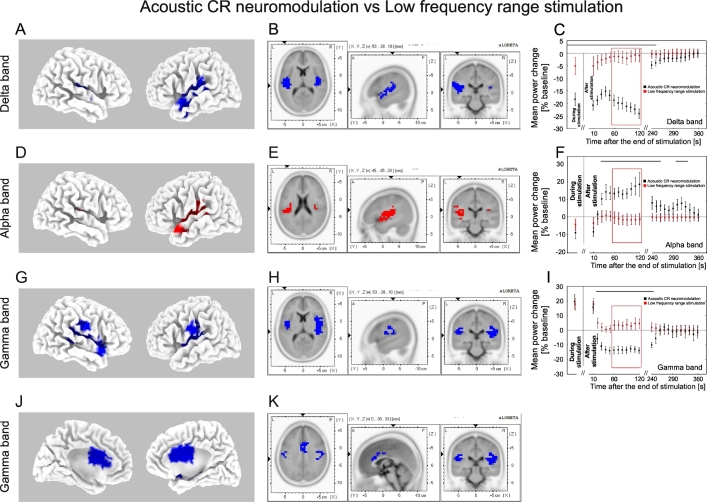
Fig. 10.
Differential changes of EEG power for the acoustic CR neuromodulation and LFR-stimulation. The effect of acoustic CR neuromodulation on the sLORETA mean current source density as compared to the LFR-stimulation (format as in Fig. 9). Delta decrease (indicated by blue voxels) was significantly greater after acoustic CR neuromodulation as compared to the LFR-stimulation (A, B). Alpha increase (indicated by red voxels) was significantly greater after acoustic CR neuromodulation as compared to the LFR-stimulation (D, E). Gamma decrease (indicated by blue voxels) was significantly greater after acoustic CR neuromodulation as compared to the LFR-stimulation (G, H, J, K). Time course of the mean delta (C), alpha (F) and gamma (I) power during (averaged over the whole stimulation period) and after the end of acoustic CR neuromodulation (black) and the LFR-stimulation (red) expressed as a percentage change from the baseline activity. Significant differences in power between acoustic CR neuromodulation and the LFR-stimulation are marked with the horizontal black line on the top of the plot (C, F, I).