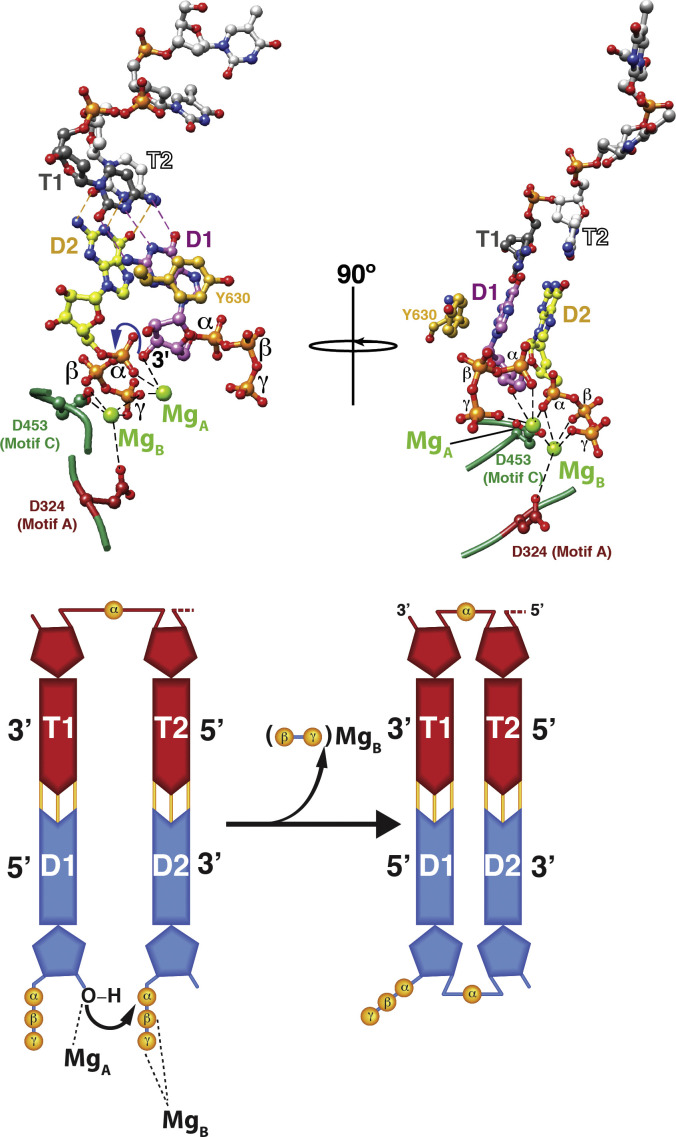
Fig. 5.
Phosphodiester bond formation. The substrate NTPs (D1 and D2) that would form the first two bases of the daughter chain are paired with the two bases (T1 and T2) at the 3′-end of the template. This priming platform is stabilized by Y630 from the C-terminal domain that base stacks with D1. The nucleotidyl-transfer reaction requires two Mg2+ ions − one (MgA) that coordinates the 3′-OH of NTP D1 and the α-phosphate of the NTP D2; a second (MgB) that coordinates the β- and γ-phosphates of NTP D2 in addition to the sidechains of the conserved motif A (D324) and motif C (D453) aspartates. Coordination with MgA lowers the pKa of the 3′-OH of NTP D1 enabling a nucleophilic attack on the α-phosphate of D2 creating a phosphodiester bond between the two NTPs. The pyrophosphate product is stabilized by MgB. The nucleotidyl-transfer reaction is shown schematically in the lower panel.