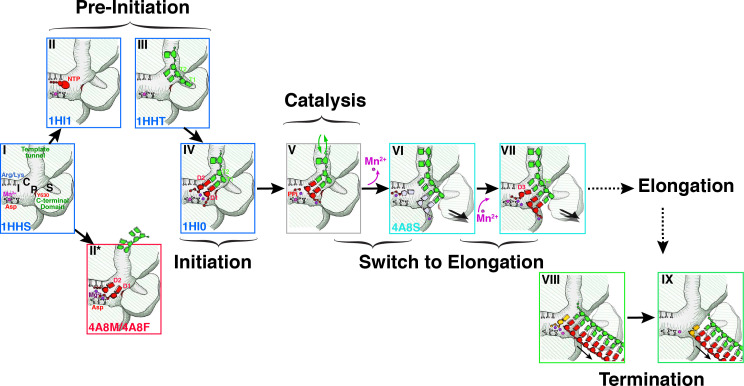
Fig. 6.
Proposed sequence of events in P2 mediated RNA synthesis. I, C, P and S indicate the 2nd NTP binding site (I-site or interrogation-site, formed by motif F), the catalytic NTP binding site (C-site or catalytic-site, formed by the motif C G/SDD triplet), the priming platform (P-site, formed by Y630 on the CTD) and the specificity pocket (S-site, also part of the CTD), respectively. In State I, free P2 is complexed with the structural Mn2+ ion located in its non-catalytic binding-site with the CTD in a closed conformation. Under these conditions P2 rapidly samples states II, II* and III corresponding to NTP and template-bound conformations (pre-initiation). In state III, the template bound-state of P2, the 3′-end of the template overshoots the active site and is locked into the specificity pocket (S-site). Metal ions at non-canonical sites facilitate the transit of NTPs through the substrate portal. Step IV: The template ratchets back to allow Watson-Crick base pairing of its 3′-end with the complimentary NTPs (D1 and D2). At this state the catalytic Mg2+ ions are drawn into their appropriate position and the non-catalytic position is occupied by Mn2+. Step V: The nucleotidyl-transfer reaction occurs with the formation of a phosphodiester bond between D2 and D1 with the release of pyrophosphate. Step VI: In order to allow the nascent dsRNA to move forward in register to prime the system for the next nucleotidyl-transfer reaction, the destabilizing effect of the Mn2+ facilitates the opening of the CTD. Mn2+ ions lost at this stage need to be replaced by external Mn2+. The initiation complex is still not stable enough to transit into its processive, elongation stage. Step VII: A new substrate NTP (D3) complementary to the third template base from the 3′-end (T3) now forms a new initiation complex culminating in a repeat of IV–VI and leading to a phosphodiester bond formation between D3 and D2. At this stage (or in cases after a few more cycles) the complex is stable, the CTD is fully open and the Mn2+ is stably bound at the non-catalytic binding site. At this point P2 enters the elongation stage where the entire template can be read through. The alphanumeric codes in the bottom left-hand corner of each box, where present, represent the PDB accession codes of the structures, where available), used to characterize the corresponding step. Modified from Wright et al. (Wright et al., 2012) with permission. Step VII: after the entire daughter strand complimentary to the template has been synthesized, the TNTase activity of P2 attaches a nucleotide to its 5′-end. Step VII: The dsRNA leaves P2. Steps VII and VIII have been proposed to comprise the termination step in RNA synthesis (Poranen et al., 2008a).