Figure 1.
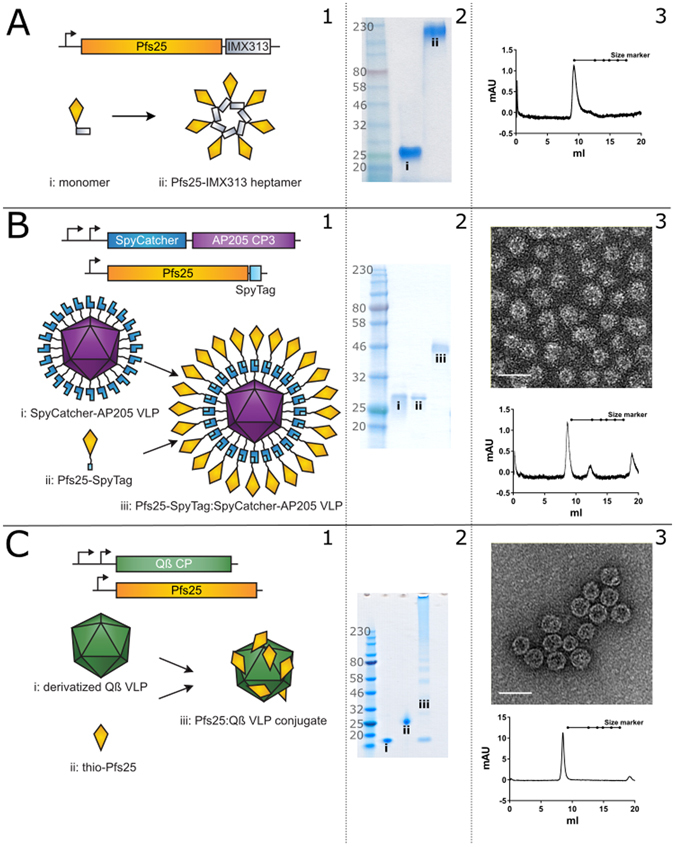
Generation and characterisation of nanoparticles used in this study. (A) Pfs25-IMX313 (1). Schematic of construct design particle and formation illustrating monomer (i) and heptamer (ii). (2) SDS-PAGE showing reduced monomer (i) and non-reduced heptamer (ii). (3) Size exclusion chromatography trace illustrating heptamer migration in the expected range. (B) Pfs25-SpyTag:SpyCatcher-AP205 (1) Schematic of construct design and particle formation illustrating SpyCatcher-AP205 (i), Pfs25-SpyTag (ii), and Pfs25-SpyTag:SpyCatcher-AP205 conjugate (iii). (2) Reducing SDS-PAGE showing SpyCatcher-AP205 (i), Pfs25-SpyTag (ii), and Pfs25-SpyTag:SpyCatcher-AP205 conjugate (iii). (3) Negatively stained TEM of Pfs25-SpyTag:SpyCatcher-AP205, scale bar = 50 nm and size exclusion chromatography trace illustrating VLP migration in the expected range. (C) Pfs25-Qβ (1) Schematic of construct design and particle formation illustrating Qβ VLPs (i), Pfs25 (ii), and Pfs25-Qβ conjugate (iii). (2) Reducing SDS-PAGE showing Qβ VLPs (i), Pfs25 (ii), and Pfs25-Qβ conjugate (iii). (3) Negatively stained TEM of Pfs25-Qβ VLPs, scale bar = 50 nm and size exclusion chromatography trace illustrating VLP migration in the expected range. Numbers at the left of the coomassie images represent size in kDa. Size markers in all size exclusion traces are from left to right: 670, 158, 75, 44, 29 and 13.7 kDa.
