Figure 4.
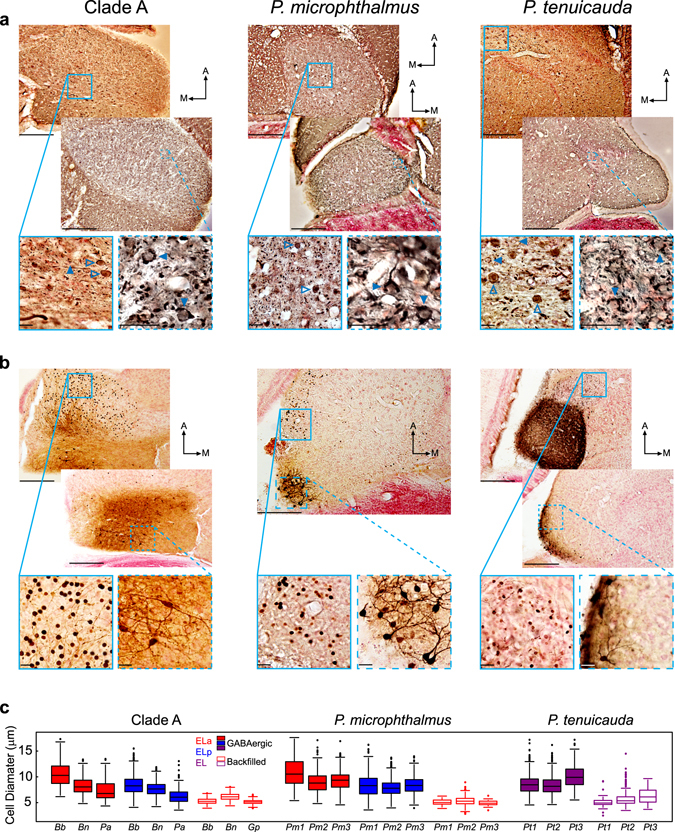
The three same basic types of neurons are found in ELa/ELp of clade-A species and P. microphthalmus, and in EL of P. tenuicauda. (a) GABA immunohistochemistry revealed inhibitory neurons in ELa and ELp of clade-A species (left) and P. microphthalmus (center), and throughout EL and the lateral lemniscus of P. tenuicauda (right). The images on the bottom show enlarged views taken from the boxes and show stained somas (open arrowheads) and terminals onto unstained cell bodies (filled arrowheads). (b) Iontophoretic injections in ELp of clade-A species and P. microphthalmus, and in the posterior end of EL of P. tenuicauda reveal multipolar cells in ELp and the posterior end of EL, and backfilled adendritic small cells in ELa and the anterior end of EL. Images on the bottom are enlarged views taken from the boxes and show stained somas of backfilled small cells (left), and multipolar cells (right). All photomicrographs in (a) and (b) are from 50-µm horizontal sections through the midbrain. (c) Cell diameters of GABAergic cells (filled boxes) and backfilled cells (open boxes) after injections of neuronal tract tracers in ELp and the posterior end of EL. Cell diameters in (c) were measured in ELa (red) and ELp (blue) of clade-A species and P. microphthalmus, and in EL (purple) of P. tenuicauda. Data of GABAergic cells were obtained from one B. brachyistius (Bb), one B. niger (Bn), and one P. adspersus (Pa) for clade A, from three individuals of P. microphthalmus (Pm1-3), and from three individuals of P. tenuicauda (Pt1-3). Data of backfilled cells that project to multipolar cells were obtained from one B. brachyistius (Bb), one B. niger (Bn), and one G. petersii (Gp) for clade A, from three individuals of P. microphthalmus (Pm1-3), and from three individuals of P. tenuicauda (Pt1-3). In (a) and (b), scale bars in top photomicrographs represent 200 µm and scale bars in the enlarged photomicrographs represent 20 µm. Clade-A species represented are B. brachyistius (left) and B. niger (right) in (a) and B. brachyistius in (b). Photomicrographs in (a) come from one B. brachyistius (left) and one B. niger (right) for clade A, one P. microphthalmus, and two P. tenuicauda. Photomicrographs in (b) come from one B. niger, one P. microphthalmus, and two subjects of P. tenuicauda. The injection sites are not visible in these sections. Injection sites in (b) were: towards the middle of ELp and 350 µm ventral with respect to the top photomicrograph from clade A; towards the lateral and posterior edge of ELp and 350 µm ventral relative to the photomicrograph of P. microphthalmus; towards the medial and posterior edge of EL and 150 µm ventral with respect to the top photomicrograph of P. tenuicauda; and towards the lateral and posterior edge of EL and 150 µm ventral relative to the bottom photomicrograph of P. tenuicauda. A: anterior. M: medial.
