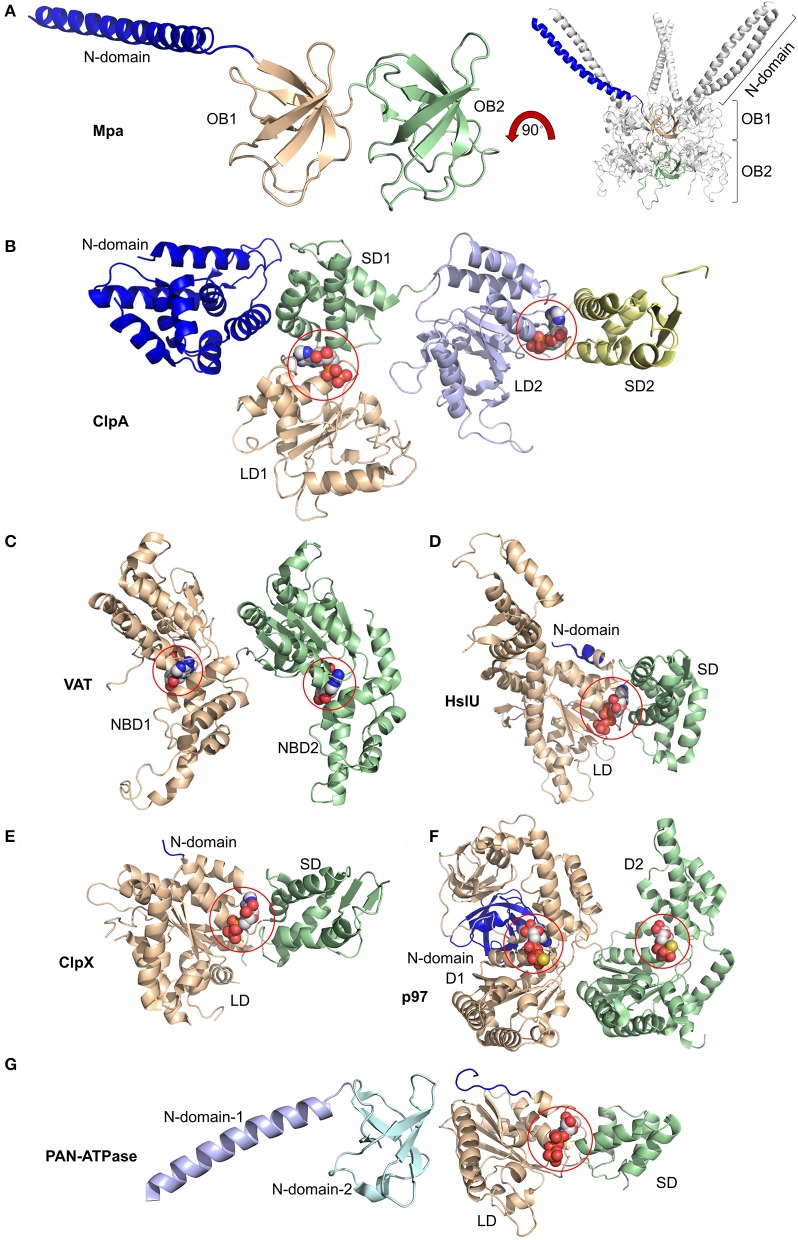
Figure 2.
Domain organization of AAA-ATPases. (A) Magnified view of the monomer (left) and overall view of the oligomer (right) of Mpa containing two OB rings, OB1 and OB2, along with the N-terminal coiled-coils (blue). Magnified views of monomers bound to nucleotides highlighted by spheres of (B) ClpA with small and large domains SD1, SD2, LD1, and LD2 bound to ADP at the SD1/LD1 and SD2/LD2 interfaces; of (C) Valosin-containing protein-like ATPase (VAT) with nucleotide binding domains NBD1 and NBD2 bound to ATP; of (D) HslU with N-terminal (N), large (LD), and small (SD) domains and ATP; of (E) ClpX with N-terminal (N), large (LD), and small (SD) domains with ADP; of (F) p97/VCP/Cdc48 with N-terminal (N) and domain-1 (D1) and -2 (D2) bound to ATPγS; of (G) proteasome-activating nucleotidase (PAN) with N-domains 1 (from Gcn4) and 2 and large (LD) and small (SD) domains. Again, ATP is bound at the SD/LD interface. This figure was prepared based on the availability of structures in the protein data bank using the PDB IDs: 3M9D, 1KSF, 5VC7, 1DO0, 3HWS, 5C18, 2WG5, and 2WFW through PyMOL (Ver. 1.8.0.2) molecular graphics software (Schrodinger, LLC, New York).