FIGURE 2.
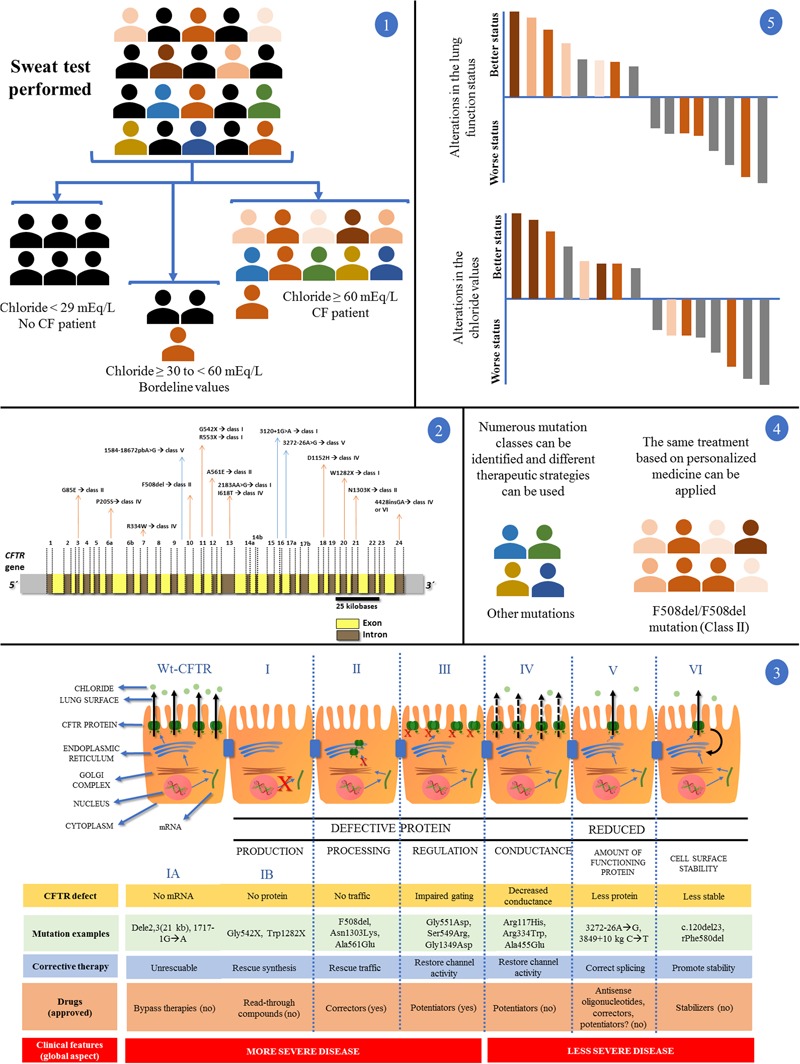
Clinical and laboratory response achieved with the introduction of personalized medicine and precision medicine in CF regarding disease diagnosis by sweat test and CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator) mutation screening. (1) In a population, patients with suspected CF underwent the sweat test. Chloride values equal to/greater than 60 mEq/L are the gold standard for CF diagnosis. Chloride values smaller than 30 mEq/L are related with normal subjects for CF diagnosis. Regarding chloride values between 30 and 60 mEq/L, nearly 5% of patients with CF show positive screening for the CFTR mutations. After the test, patients can be divided into two groups: (i) normal and borderline values for chloride test without CF diagnosis (black color); (ii) patients with CF (color symbols + some patients with CF and borderline values in the sweat test). (2) Patients with CF, in some centers around the world, can undergo the CFTR genetic screening. The figure shows the CFTR gene containing introns (yellow) and exons (brown). Some mutations and their locations were shown. The main CFTR mutation is the F508del, which affects most patients with CF. (3) First is shown the CFTR protein mechanisms from transcription to cell surface anchoring and function. Defective CFTR protein is observed followed by class I, II, III, and IV. Reduced CFTR protein function is observed followed by class V and VI. Class I: No production by no transcription (IA, no mRNA; IB, no protein). Class II: CFTR processing error. CFTR protein is degraded in endoplasmic reticulum. Class III: CFTR protein regulation with defect. CFTR mutations related with the R domain expression. Class IV: conduction is altered by mutations related by membrane-spanning domains. Class V: reduced amount of CFTR protein at cell surface – however, normal activity is present. Class VI: low CFTR function stability. CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator; red (X) indicates absence of CFTR protein by premature stop codon (class I), absence of CFTR protein at cell surface (class II) or absence of CFTR function (class III); black continuous arrows indicate normal chloride transport; black no continuous arrows indicate residual chloride transport. The number of CFTR protein at cell surface is related with CFTR gene expression. Moreover, there is a short description regarding the CFTR defect, mutation examples, corrective therapy, drugs, and clinical features. (4) After the CFTR genetic screening we can divide the patients with CF according to CFTR mutation classes, additionally, in each class we can perform the direct treatment. The figure shows a patient group with the F508del/F508del genotype and another group with numerous genotypes. By personalized medicine, we can treat the patients regarding the CFTR mutation class (in theory), and, in some cases, we can develop the drug for specific CFTR mutations. (5) Regarding only patients with CF and F508del/F508del genotype, after the use of the new drugs (i.e., VX809-VX770), we can achieve patients with CF plus positive response and negative response using or not the drugs comparing the results with placebo (gray data). In this case, the F508del/F508del genotype (orange data) has a wide variability in the drug response dependent on the mutual action of genotype, environment, and lifestyle (intensity of the orange color). All the data can be observed in details in Boyle et al. (2014), Marson et al. (2015, 2016), De Boeck and Amaral (2016), and Farrell et al. (2017).
