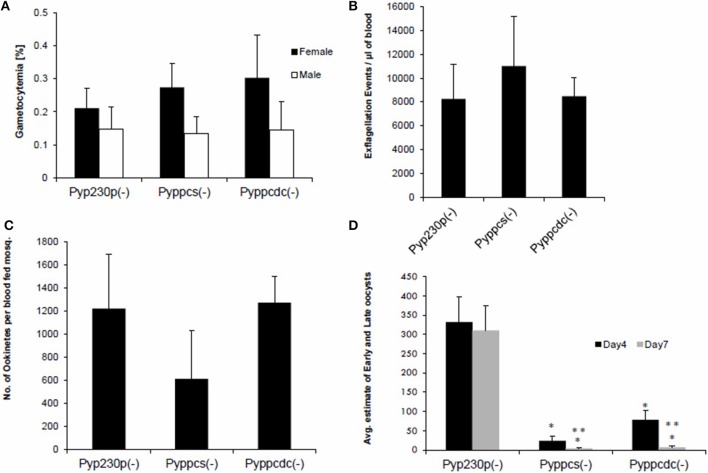
Figure 3.
Parasites lacking PyPPCS or PyPPCDC are deficient in oocyst development. (A) Graph shows average percentages of male and female mature gametocytes in thin smears from groups of SW mice IV injected 3 days earlier with 106 infected erythrocytes with Pyppcs(−), Pyppcdc(−), or Pyp230p(−) (all are G5 passages). No statistical significant difference is detected among strains tested in sexual stages development in blood. (B) Graph shows average number of male gamete exflagellation events per μl of mouse blood determined by a hemocytometer using 1:10 dilution of tail blood. No statistical significant difference in male gamete exflagellation is detected in Pyppcs(−) or Pyppcdc(−) strains compared to Pyp230p(−). (C) Graph shows average number of ookinetes per mosquito dissected out 20 hours pmf with no statistical significant difference among strains tested. Results in graphs (A–C) confirm that the development of sexual stages and ookinetes is not affected by the deletion of PPCS or PPCDC. (D) Graph shows the average number of early oocysts developing on midguts of mosquitoes infected with Pyppcs(−), Pyppcdc(−), or Pyp230p(−) strains at days 4 and 7 pmf detected using fluorescence microscopy. Statistical significant reduction (denoted by *) in the number of developing oocysts is detected in Pyppcs(−) or Pyppcdc(−) strains compared to Pyp230p(−) at days 4 and 7 pmf, respectively. Further statistical significant reduction (denoted by **) in the number of developing oocysts at day 7 compared to day 4 pmf is detected in each of the strains Pyppcs(−) and Pyppcdc(−) but not in Pyp230p(−) strain. The mean values for all parasite strains were analyzed with the One-Way Analysis-of-Variance (ANOVA) and statistical significance was set at a P < 0.05. The results shown are the mean of three independent experiments with each independent experiment involving at least three mice per parasite strain, error bars represent standard deviation.