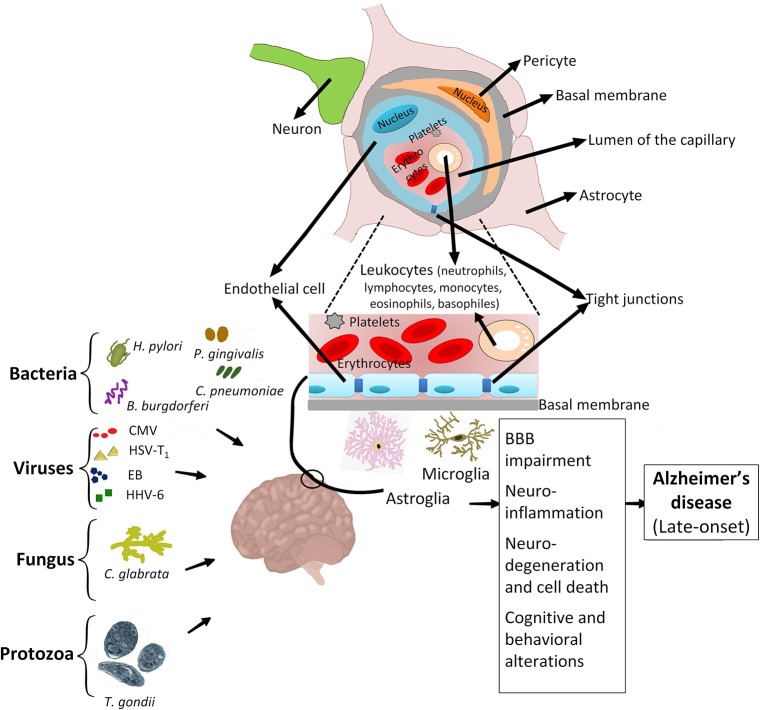
Figure 2.
Association of infectious agents with Alzheimer's disease. Chronic infections caused by major infectious agents, i.e., Helicobacter pylori, various types of spirochetes, including periodontal pathogen spirochetes and Borrelia burgdorferi, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Cytomegalovirus, Herpes simplex virus type 1, Epstein-Bar virus, Human herpes virus 6, Candida glabrata and Toxoplasma gondii are associated with development of AD. Early life exposure to these pathogenic agents can activate the resting microglia and astroglia, trigger the migration of immune cells to the neuro-endothelial tissue, degrade cell-cell tight junctions, and cause the breakdown of BBB. These activities result in development of various side effects such as neuronal damage, neuroinflammation and ultimately predispose the adult patient to develop AD.