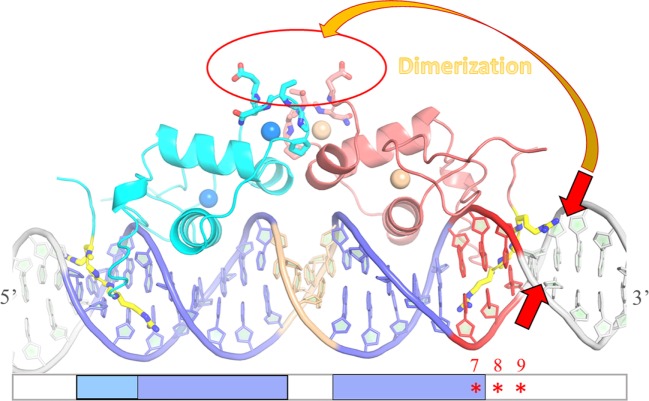
Figure 8.
Schematic drawing of the influence of DNA shape on dimer stabilization. Model of the ERRα DNA-binding domain (DBD) dimer on DNA based on the structure of ERα DBD-IR3 response elements (RE) (PDB code 1HCQ), where the nuclear magnetic resonance structure of ERRβ DBD (PDB code 1L01) is superimposed to each of the two subunits of ERα DBD-IR3 RE. An ideal B-DNA model is used in the drawing. Comparative analysis of the residues of the D-box involved in dimerization between ER and ERR suggests that ERRα DBD could a priori dimerize in a way similar to that seen in the structure of ERα DBD, without any structural impediment (red circle). On the other hand, the stabilization of ERRα DBD dimer on DNA is influenced by the sequence-dependent DNA shape of the second ERR-binding site at the 3′-end of DNA. The local geometry of the minor groove that encompasses the second half-site and the flanking nucleotides (especially between positions + 5 and + 9) is crucial for the formation of an ERRα DBD dimer on DNA. Sequence-driven narrow minor grooves at this location (small red arrows) favor dimer stabilization (large orange arrow).