Figure 7. IL-22 activates macrophages for Mtb control.
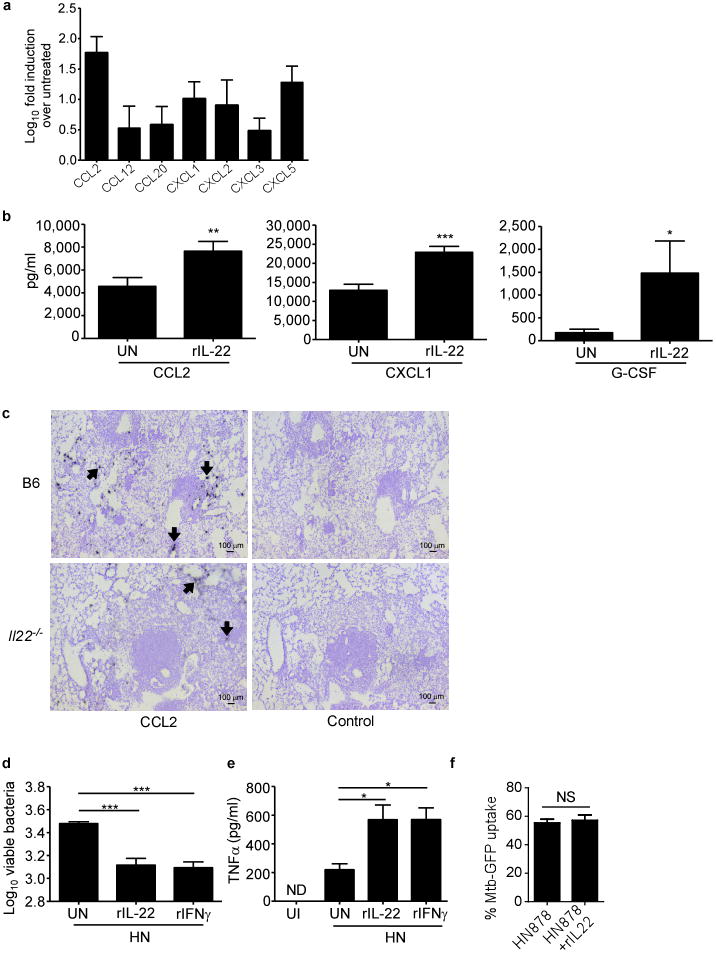
Non-tumorigenic lung epithelial cell line C10 was treated with rIL-22 and (a) chemokines mRNA was determined by real-time PCR, and fold induction over untreated cells was determined or (b) protein levels were determined in culture supernatants by luminex assays. (c) Il22-/- and B6 mice were aerosol infected with ∼500 CFU of Mtb HN878 and on day 100 p.i., formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded lung sections were analysed by ISH to determine localization of CCL2 mRNA expression within the lung. Black arrows indicate the localization of CCL2 mRNA within granulomas. Original magnification, × 10. BMDMs derived from B6 mice were treated with rIL-22 and infected with Mtb HN878 (MOI of 1) and (d) intracellular Mtb burden was determined by plating and (e) the protein levels of TNFα production was determined in culture supernatants by ELISA. n = 4-6. (f) B6 macrophages were pretreated with rIL-22 (100 ng/ml) for 48 hrs and then infected with HN878:GFP at an MOI of 1 for an additional 4 hours, percent Mtb:GFP uptake was assessed. ND, not detected; UI, uninfected; UN, untreated; NS = not significant. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001 by (d,e) one-way ANOVA or (b,f) students t test. Error bars represent standard deviation. Representative individual experiments are shown from at least one experiment.
