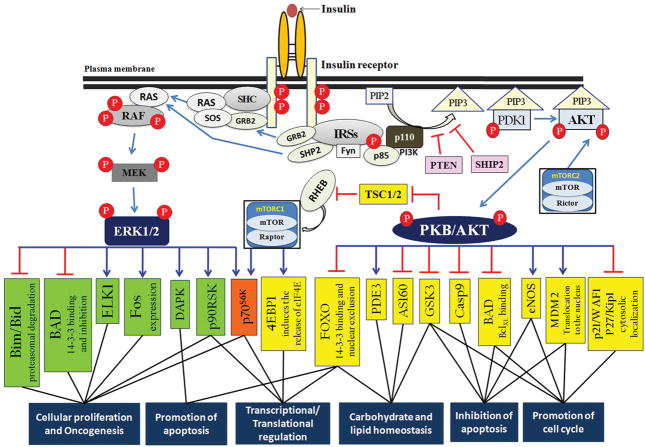
Figure 1.
Insulin-dependent signal transduction pathways. IR undergoes autophosphorylation and activation at the C-terminal domains upon ligand binding. Tyrosine-phosphorylated adaptor proteins recruit signaling proteins via specific protein domains. Active PI3K phosphorylates the membrane phospholipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate to produce the second messenger PIP3. Phospholipid phosphatases (e.g., phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 [PTEN] and SH2 domain-containing inositolphosphatase-2) dephosphorylate and convert PIP3 to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, and negatively regulate the PI3K pathway. PIP3 recruits phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 (PDK1) and AKT to the plasma membrane, where PIP3-bound AKT is phosphorylated at Thr308 by PDK1 and Ser473 by Rictor-mTORC2. Activated AKT phosphorylates and regulates many target proteins (yellow and orange box(es)) either positively (→) or negatively (⊣) to mediate distinct biological events, including (i) maintenance of glucose homeostasis; (ii) cellular survival and growth; (iii) inhibition of apoptosis; (iv) angiogenesis; and (v) regulation of gene transcription and protein synthesis. AKT provides a direct link between insulin signaling and nutrient sensing. The ERK signaling pathway is triggered by activation of the small GTPase protein p21 RAS. Active diphosphorylated ERK shuttles between the cytoplasm and nucleus, and regulates substrate proteins in both compartments (green and orange boxes), to mediate cell growth, survival, and differentiation. 4EBP1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1; Casp9, Caspase9; DAPK, death-associated protein kinase; eIF4E, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase 3; MDM2, mouse double minute 2 homolog; p90RSK, ribosomal protein S6 kinase; RHEB, RAS homolog enriched in brain; SHC, SH2 domain-containing; SHIP2, SH2 domain-containing inositolphosphatase-2; SOS, son of sevenless.