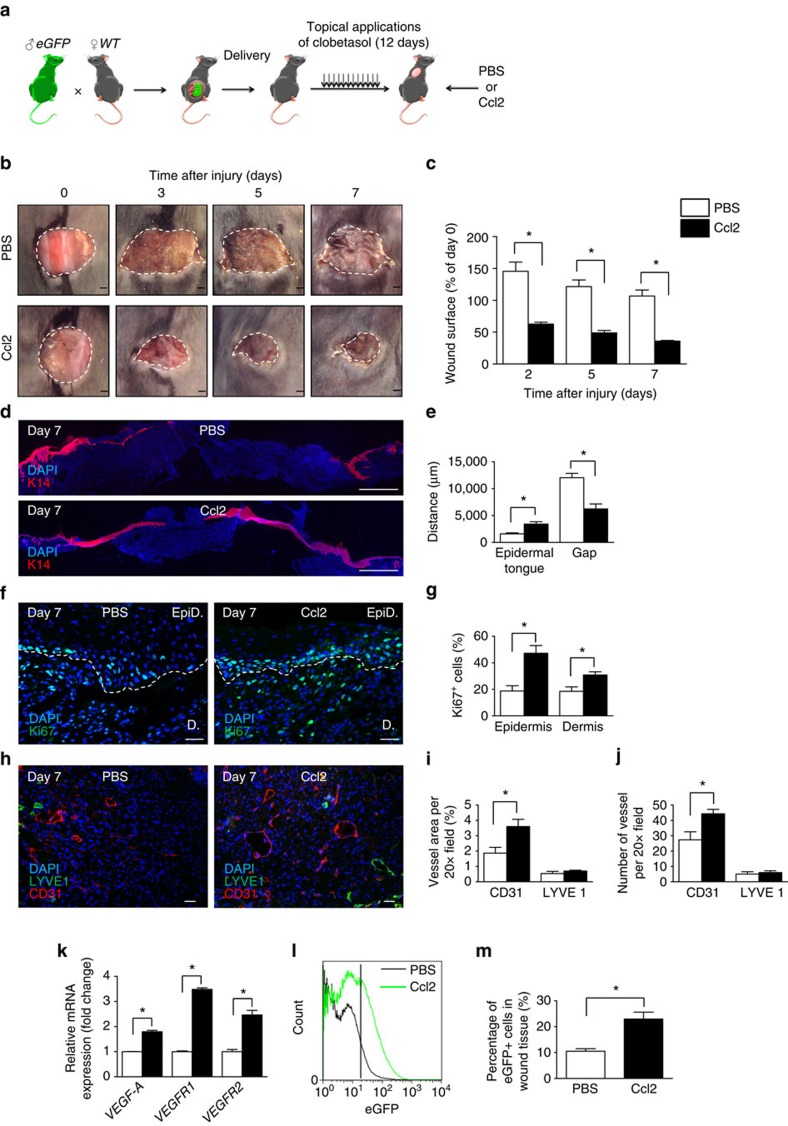
Figure 6. Ccl2 improves delayed wound healing in postpartum conditions by recruiting FMCs.
(a) Experimental design: Each mouse received 12 daily topical applications of dermoval cream after the delivery. An 8 mm wound was created on the clobetasol-treated skin of the female mice postpartum (these mice had carried eGFP+ foetuses) and we injected PBS or Ccl2 into the lesion immediately and 2 days after skin excision. (b) Time course analysis of the healing of the excisional skin lesion; a representative image is shown. Scale bars: 1 mm. (c) Planimetry of the wound area relative to the initial wound area at each time point (n=5). (d) Anti-K14 (red) labelling of neoepidermal tongues and gaps in the wound on day 7. Scale bars: 1 mm. (e) Measurement of neoepidermal tongues and gaps (n=4). (f) Anti-Ki67 (green) labelling of the wound. Scale bars: 50 μm. (g) Quantification of Ki67+ cells in epidermal wound edges (EpiD) and the dermal granulation tissues (D) (n=3). (h) Dual labelling for CD31 (red) and LYVE1 (green). Scale bars: 50 μm. (i) Quantification of relative vessel area per 20 × field by fluorescence densitometry (n=3). (j) Quantification of the number of vessel types per 20 × field (n=3). (k) Quantitative RT–PCR analysis of VEGF-A, VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 mRNA levels normalized against mRNA levels for Gapdh (n=3). (l) FACS analysis demonstrated the presence of a significantly larger number of eGFP+ cells in the wounds of postpartum mice treated with Ccl2 than in those treated with PBS (n=3). (m) Quantification of eGFP+ cells in the wounds of postpartum mice receiving injections of PBS or Ccl2 (n=3). Student's t-test, *P<0.05; mean±s.e.m.