Figure 3.
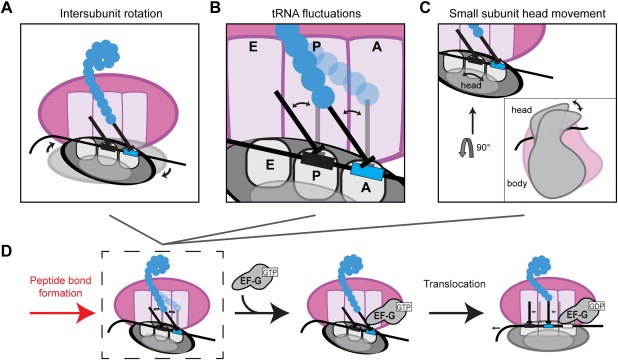
Conformational changes in the ribosome during translocation. Peptide bond formation unlocks the ribosome allowing ribosome intersubunit movements between the nonrotated and rotated states (A), movements of the A‐site and P‐site tRNAs between the classical (A/A, P/P) and hybrid (A/P, P/E) conformers (B), and swiveling of the head domain of the small subunit (C). EF‐G binding stabilizes the hybrid rotated state (D) and translocation via GTP hydrolysis brings the ribosome back to the nonrotated state, with the tRNAs in the classical conformation.
