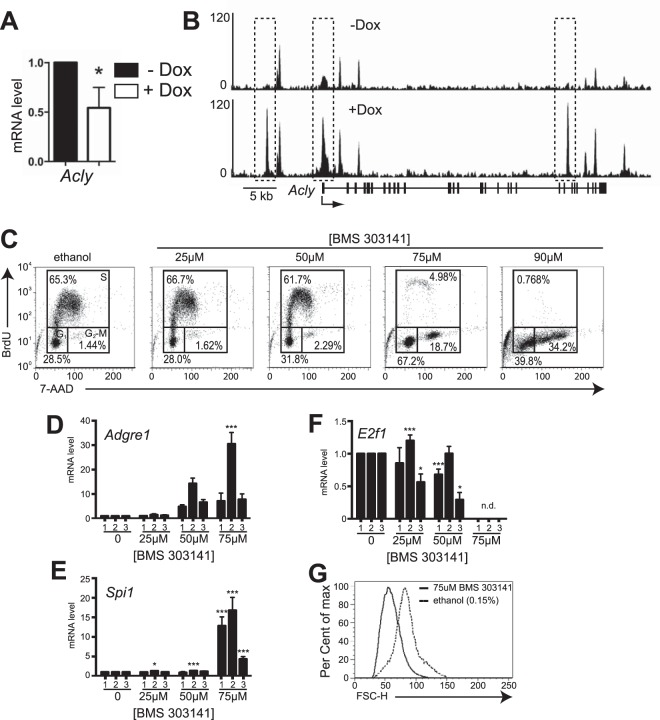
FIG 4.
Inhibition of ATP citrate lyase activity induces cell cycle arrest and differentiation in BN cells. (A) Induction of PU.1 expression in iBN cells reduces Acly mRNA transcript levels. Acly mRNA transcript levels were determined using RT-qPCR of RNA prepared 72 h after induction of PU.1 with 1,000 ng/ml Dox. (B) PU.1 association with the Acly locus is inducible. Shown are ChIP-seq tracks without (−) and with (+) Dox 72 h after PU.1 induction. The Acly gene structure is shown below the bottom panel; vertical boxes represent exons. The dotted box indicates the site of increased PU.1 association. (C) Inhibition of ATP citrate lyase (ACL) activity induces cell cycle arrest in BN cells. BN cells were treated with the ACL inhibitor BMS303141 at the indicated concentrations for 48 h before cell cycle analysis using flow cytometry. The control was 0.01% ethanol. One representative experiment is shown. (D to F) Induction of myeloid differentiation in BN cells by ACL inhibition. Shown are fold changes in mRNA transcript levels of Adgre1, Spi1, and E2f1 normalized to the B2m transcript level in three independent experiments, indicated by numbers 1 to 3. mRNA transcript levels were measured 48 h after treatment with the indicated concentrations of BMS303141. n.d., not detected. (G) ACL inhibition reduces cell size. Flow cytometry was used to determine relative cell size as measured by forward scatter (FSC-H) 48 h after inhibition of ACL activity by 75 μM BMS303141 in BN cells. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001.