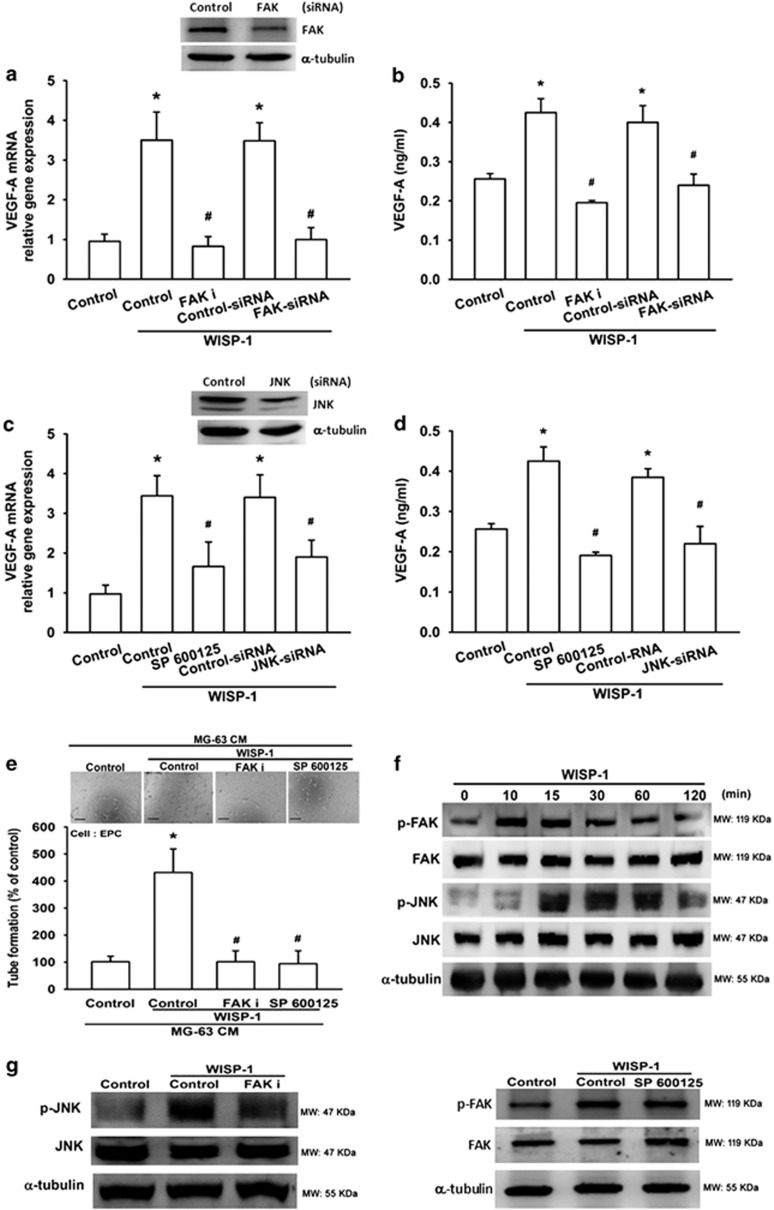
Figure 3.
FAK and JNK signaling pathways are involved in WISP-1-induced VEGF-A expression and angiogenesis. (a and b) MG-63 cells were pretreated with a FAK inhibitor (FAK i; 10 μM) for 30 min or a FAK siRNA for 24 h, before treatment with WISP-1 (30 ng/ml) for 24 h. mRNA was quantified using RT-qPCR and VEGF-A protein expression was assayed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Untreated cells were used as the control. (c and d) MG-63 cells were pretreated with a JNK inhibitor (SP600125; 10 μM) for 30 min or a JNK siRNA for 24 h, before treatment with WISP-1 (30 ng/ml) for 24 h. mRNA was quantified using RT-qPCR and VEGF-A protein expression was assayed by ELISA. Untreated cells were used as the control. (e) MG-63 cells were pretreated with a FAK i or SP600125 for 30 min, then treated with WISP-1 (30 ng/ml) for 24 h. Culture medium was collected as CM and then applied to EPCs for 24 h. EPC capillary-like structure formation was examined by tube formation (bar=100 μm). CM collected from untreated cells was used as the control. (f) MG-63 cells were incubated with WISP-1 (30 ng/ml) for the indicated times; FAK and JNK phosphorylation was detected by western blot (MW, molecular weight). (g) Cells were pretreated for 30 min with FAK i or SP600125, followed by stimulation with WISP-1 (30 ng/ml). p-FAK and p-JNK expression were detected by western blot. Each experiment was performed in triplicate (N=3). Results are expressed as the mean±S.E.M. *P<0.05 compared with control; #P<0.05 compared with the WISP-1-treated group