Figure 1.
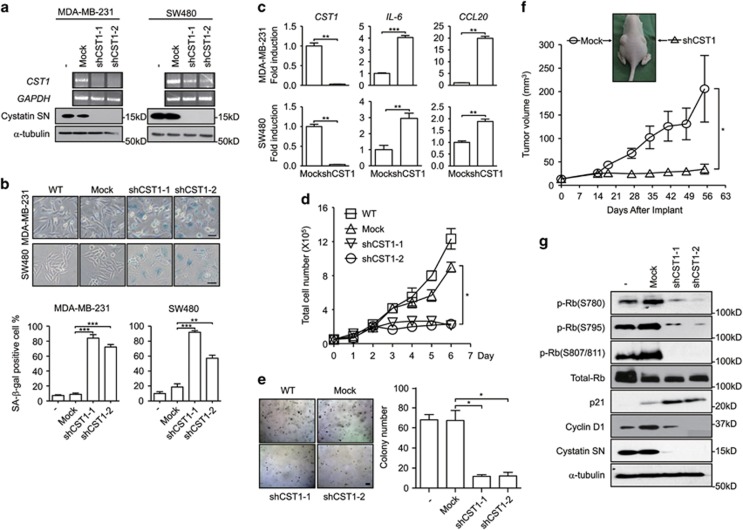
CST1 is required for cell proliferation and colony growth in vitro and in vivo. The following assays were performed in human cancer MDA-MB-231 and SW480 cells transduced with a control shRNA (mock) or an shRNA for CST1. (a) The efficiency of CST1 knockdown was confirmed by reverse transcription PCR (upper) and western blotting (lower). (b) Representative photographs of SA-β-gal staining (upper). Senescence under the indicated condition was quantified as the percentage of SA-β-gal-positive cells (lower). Scale bars, 50 μm. (c) The expression of SASP genes induced by CST1 knockdown. RNAs were extracted from cells, and real-time PCR analysis was performed to quantify the transcripts of CST1, IL-6 and chemokine ligand 20 (CCL20). (d) Analysis of anchorage-dependent cell proliferation. Cells were seeded on to six-well plates (5 × 104 cells per well) and cultured for the indicated number of days. The number of cells was counted using a hemocytometer. One-way ANOVA was used for statistical analysis (*P<0.05). (e) Analysis of anchorage-independent cell proliferation. Cells were seeded on to complete DMEM containing agarose (1 × 105 cells per well) and cultured for 12 days. Formed colonies were stained with 0.005% crystal violet and quantified under a light microscope. Scale bar, 10 μm. (f) Analysis of tumor growth in the xenograft model. MDA-MB-231 cells transduced with a control shRNA or shCST1 (1 × 106 cells) were subcutaneously implanted into the left or right flanks of athymic nude mice (n=8). Tumor volume was measured on the indicated days. One-way ANOVA was used for statistical analysis (*P<0.05). (g) Protein expression of p-Rb, total Rb, p21, cyclin D1 or CST1 was evaluated by western blotting. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 by Student's t-test