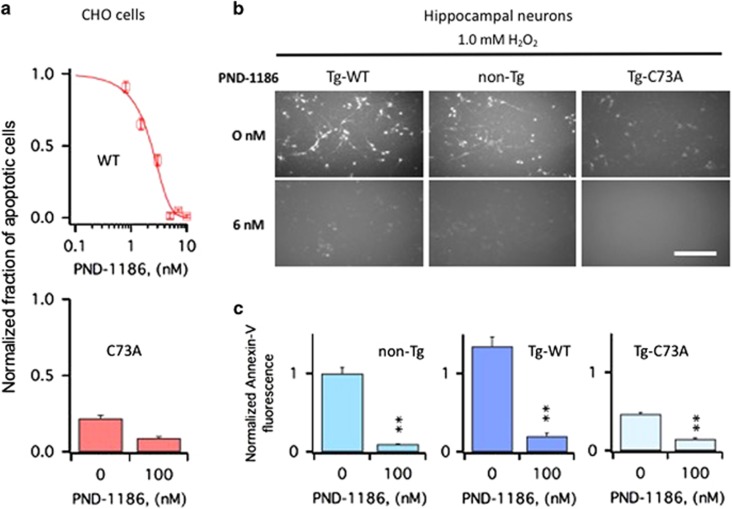
Figure 4.
PND-1186 protects CHO cells and primary hippocampal neurons from apoptosis induced by oxidation of KCNB1. (a) Upper panel: number of cells positive to Annexin-V in WT-transfected CHO cells subjected to an oxidative challenge in the absence/presence of varying concentrations of PND-1186. Data are normalized to the number of cells positive to Annexin-V in the absence of PND-1186. Data were fit to a sigmoidal function (equation (1)) with an IC50=1.95 nM. N=3 experiments. Lower panel: number of C73A-transfected CHO cells positive to Annexin-V subjected to an oxidative challenge in the absence or presence of 6 nM PND-1186. N=3 experiments. (b) Representative examples of Annexin-V staining in the primary hippocampal neurons of the indicated genotypes. The cells were exposed to 1.0 mM H2O2 for 5 min, incubated 6 h in the presence of 6 nM PND-1186, stained with Annexin-V and photographed. Size bar 100 μm. (c) Quantitative assessment of Annexin-V fluorescence in the primary hippocampal neurons of the indicated genotypes subjected to an oxidative challenge in the absence/presence of 6 nM PND-1186. Annexin-V fluorescence was calculated using the ImageJ software and data are normalized to non-Tg neurons in the absence of PND-1186. P=3.9 × 10−7 (one-way analysis of variance); **P<0.01 (Tukey's post hoc). N=3 embryos/genotype