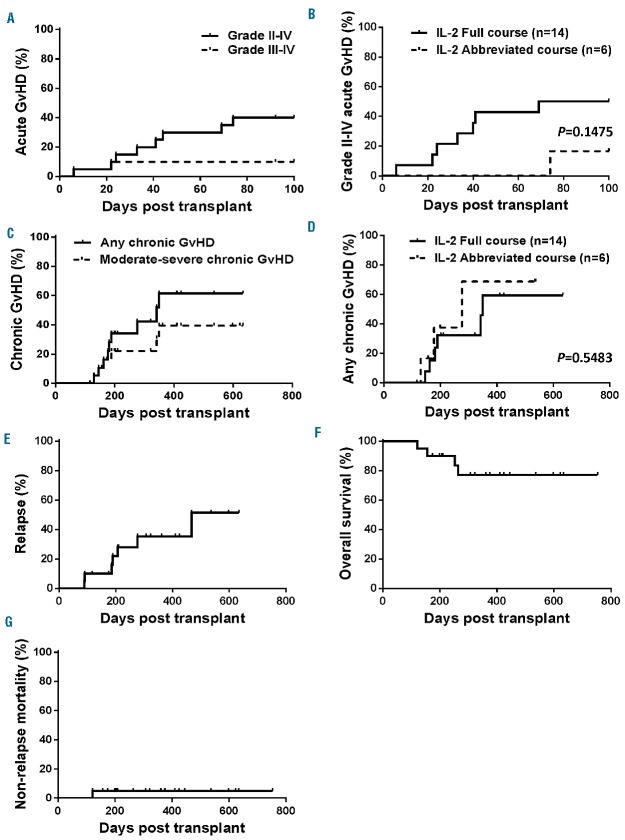
Figure 2.
The addition of prolonged IL-2 therapy with sirolimus/tacrolimus (SIR/TAC) does not further reduce acute or chronic graft-versus-host disease. (A) Cumulative incidence of acute graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is shown for grade II-IV disease (solid) and severe grade III-IV acute GvHD (dashed line) by day +100 (P=0.1177). The incidence of grade II-IV acute GvHD with IL-2/SIR/TAC [40% (95%CI: 15.8%–63.4%)] is not significantly different from our published data with SIR/TAC [43% (95%CI: 27%–59%)] alone. The acute GvHD characteristics, including organ stage, are detailed in Table 2. (B) Cumulative incidence of grade II-IV acute GvHD among patients who received a full course of IL-2 versus those who prematurely stopped (abbreviated course) IL-2 [16.7% (95%CI: 0.001–77.7) vs. 50% (95%CI: 27.8–77.1), P=0.1475]. (C) Cumulative incidence of chronic GvHD (median follow up of 470 days) based on any chronic GvHD (solid black line) or moderate to severe disease (dashed line) (P=0.2698). (D) Cumulative incidence of chronic GvHD among patients who received a full course of IL-2 versus those who prematurely stopped (abbreviated course) IL-2 [59.4% (95%CI: 27.7–81.0) versus 68.8% (95%CI: 24.5–90.6), P=0.5483]. (E-G) Cumulative incidence of relapse, overall survival, and non-relapse mortality among those treated with IL-2/SIR/TAC.