Figure 5.
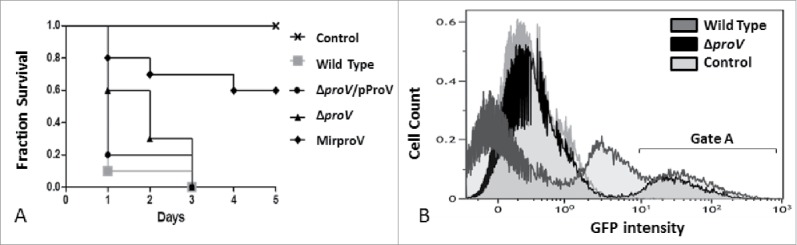
Testing S. sonnei virulence in vivo using G. mellonella larvae. (A) Fraction survival of G. mellonella larvae model challenged by 105 CFU of wild type S. sonnei strain 20071599 (gray square), the complemented strain (ΔproV/pProV) (black circle), ΔproV (black triangle) and the MirproV (black trigonal), using saline as a control (crosses). The observation lasted for 5 d. The results are means of 3 successive groups (n = 10 larvae). (B) Overlaid histogram of the flow cytometry analysis of hemocytes isolated from G. mellonella larvae mock-infected as a control (light gray), challenged by S. sonnei wild strain 20071599 (dark gray) or by ΔproV (black). Both S. sonnei strains were expressing EGFP. Hemocytes were isolated 4 hours post infection for analysis; gate A depicts hemocytes emit GFP signals.
