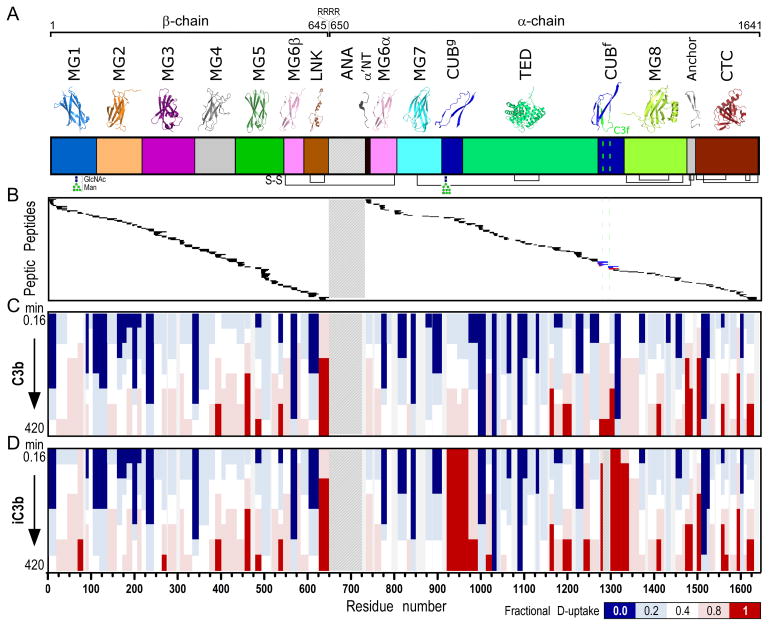
Figure 2. H-to-D exchange protection and heat map of C3b and iC3b.
A. Domain organization of C3 and its activation products (color annotation follows (2)). Ribbon representations of individual domains are shown at the top. C3b is generated upon proteolytic removal of the ANA domain (shown with a crosshatch fill pattern). β- (residues 1–645) and α-chains (residues 650–1641) are covalently linked through a disulfide bond formed between MG6 domain residues Cys537-Cys794. Further release of the heptadecapeptide C3f in the CUBf domain leads to the formation of iC3b (cleavage sites are indicated with a green dashed line). Inter- and intra-domain disulfide bonds are shown at panel bottom with black connecting lines. B. Peptic peptides of C3b and iC3b identified and analyzed for D-content. These correspond to residue numbers as indicated in the x-axis of Fig. 2D. For a detailed view of individual peptides identified and respective peptide boundaries, please refer to Fig. S1. Common peptides identified for both C3b and iC3b are indicated with black. Unique peptides of C3b (indicated with blue) and iC3b (indicated with red) were identified in the C3f-surrounding region. C, D. Heat maps of the exchange observed on the peptide level for C3b and iC3b, respectively. Color-coding is based on the fractional deuterium uptake calculated by normalizing deuterium uptake values to respective values from fully deuterated samples; each value is the average of two replicate experiments. Values for different time points of exchange are depicted; these are 0.16, 0.5, 1.7, 5, 16.7, 50, 166.7 and 420 min (from top to bottom). For simplicity, only non-overlapping peptides are shown.