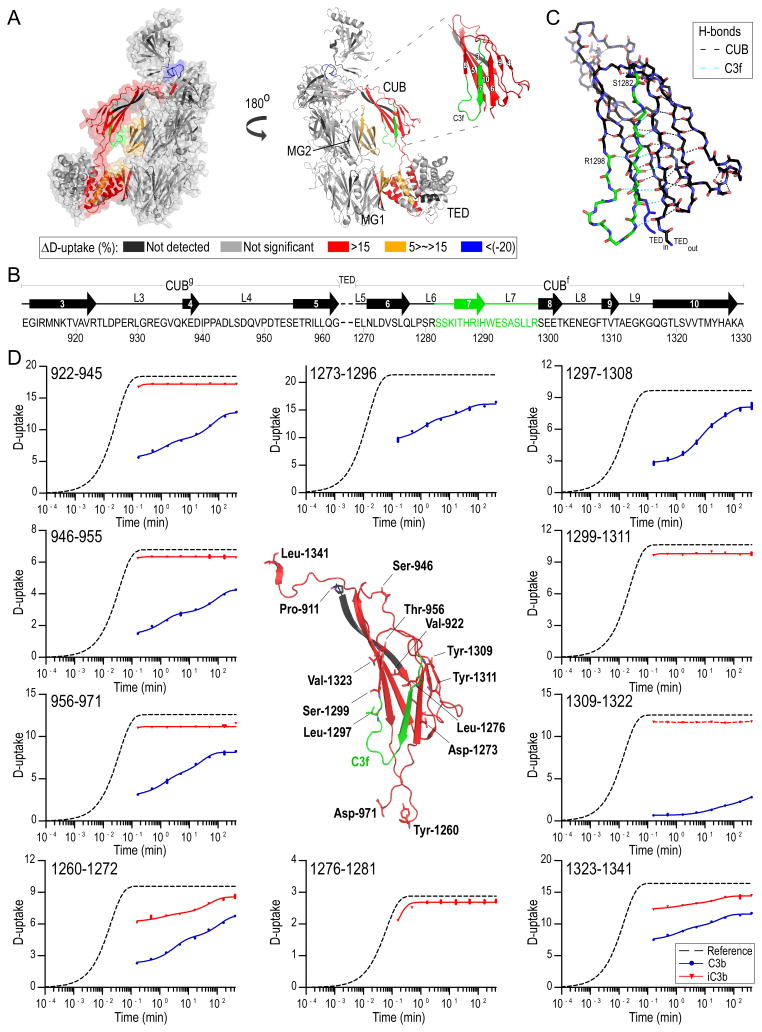
Figure 3. Differential D-uptake between C3b and iC3b.
A. Mapping of HX differences between C3b and iC3b on C3b structure; peptides with ΔD-uptake>5% are mapped on C3b [PDB: 2I07 (4), Table S1]. More exposed regions in iC3b than C3b against D-exchange are colored red, and less exposed are blue. CUB with respective fibronectin type-3 strand numbering is shown in the inset. Prominent differences in the D-exchange are detected for peptides in CUB, whereas marginal but still significant differences are detected on the interface between CUB-TED and the MG core as well as on CUB-TED inter-domain peptides. iC3b is shown to acquire a more dynamic and solvent-exposed conformation. An exception is the 1471–1480 peptide positioned between MG8 and CTC, indicating re-positioning of CTC toward the MG7/MG8 domains. B. Structural organization of the CUB domain; strand numbering follows Fig. 3A. CUBg, TED and CUBf boundaries are depicted. Loops (L) and disordered segments are marked with a solid line. C. Detailed view of the CUB structure. C3f is featured in green, and amino acids denoting the beginning and the end of the peptide are labeled. H-bonds between backbone amide hydrogens and carbonyls are depicted with black dashed lines, and those involving C3f residues with cyan; C3f participates in 9 main-chain hydrogen bonds. D. D-uptake plots of selected CUB domain peptides for C3b (blue) and iC3b (red) (for a complete list of plots, see Fig. S1). For each sequence, a reference curve (for the case of no protection) is calculated and fit to a stretched exponential equation (33). Experimental data points are similarly fit using the same β-factor calculated for the respective reference curves. Amino acids denoting the beginning of measured peptides are labeled, and their main- and side-chains are depicted with sticks. Unique peptides for C3b entailing a part (1297–1308) or the full sequence (1273–1296) of C3f are shown. Unique iC3b peptides containing the newly formed C-terminus (1276–1281) and N-terminus (1299–1311) generated upon cleavage of C3f are depicted. A curve could not be fit for peptide 1309–1322 in iC3b (indicated with a connecting red dashed line).