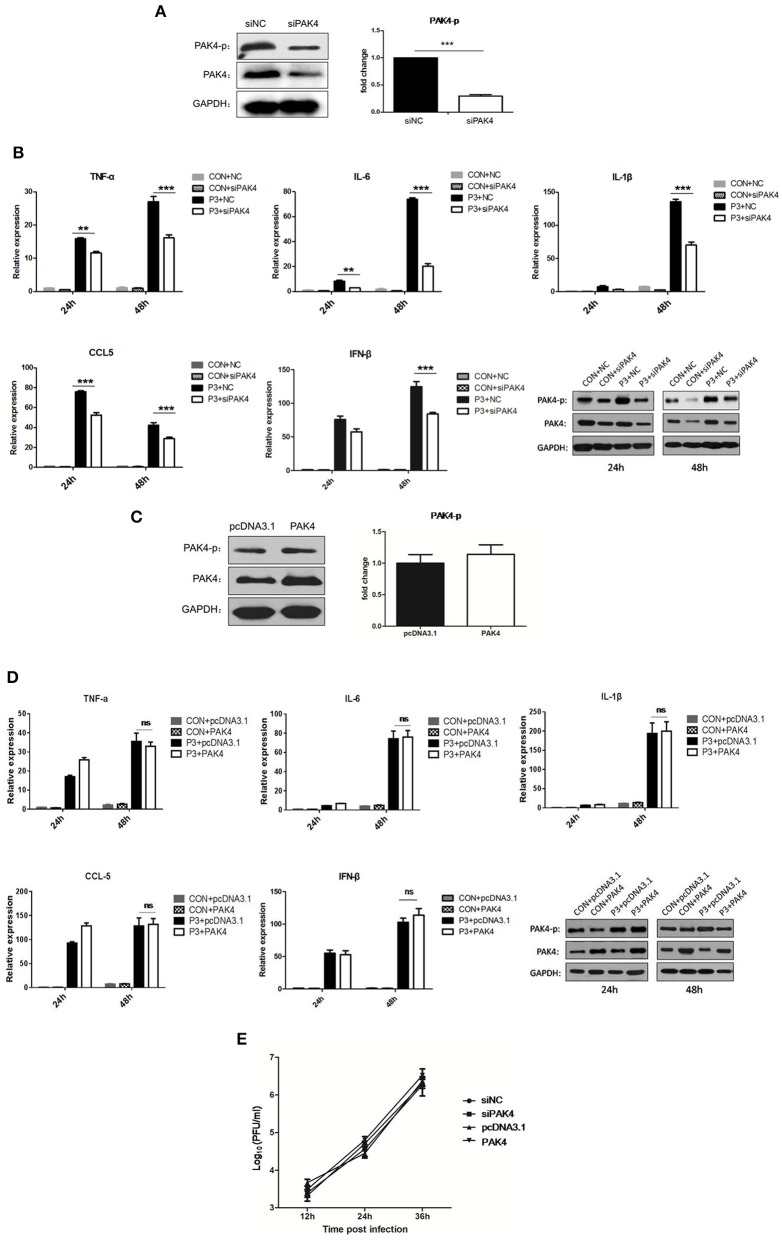
Figure 2.
PAK4 signaling contributes to JEV-induced inflammation in U251 cells. (A) U251 cells were transfected with siRNA targeting PAK4 (siPAK4) or negative control siRNA (siNC). Cells were collected at 36 h post transfection and the PAK4 was detected by Western-blot. Levels of PAK4 were quantified with immunoblot scanning and normalized to the amount of GAPDH. ***p < 0.001, compared with cells transfected with siNC (n = 3). (B) U251 cells were transfected with siPAK4 or siNC, followed by JEV infection. Cells were harvested at 24 and 48 h post infection and mRNA levels of inflammatory cytokines and IFN-β were determined by qRT-PCR. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, compared with cells transfected with siNC (n = 3). Protein levels of phospho-PAK4 and PAK4 were determined by Western-blot (downright panel). (C) U251 cells were transfected with plasmid encoding PAK4 (pPAK4) or empty vector pcDNA3.1. Cells were collected at 36 h post transfection and PAK4 was detected by Western-blot. Levels of PAK4 were quantified with immunoblot scanning and normalized to the amount of GAPDH (ns: no significant change). (D) U251 cells were transfected with plasmid encoding PAK4 or pcDNA3.1, followed by JEV-infection. Cells were harvested at 24 and 48 h post infection and mRNA levels of inflammatory cytokines and IFN-β were determined by qRT-PCR. Protein levels of phospho-PAK4 and PAK4 were determined by Western-blot (downright panel). (E) U251 cells were transfected with siPAK4, siNC, pPAK4, or pcDNA3.1, followed by JEV infection. Cell supernatants were harvested at 12, 24, and 36 h post infection and viral titers were determined by plaque assay on BHK-21.