FIGURE 2.
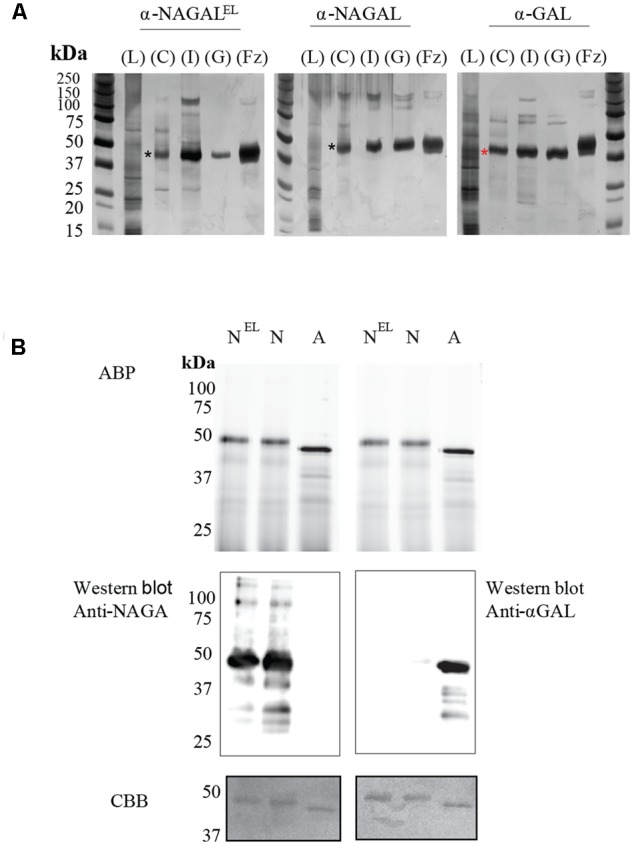
Overview of enzyme purifications: activity based probe detection, Immunoblotting and Coomassie Brilliant Blue, staining of the plant produced pure enzymes. (A) SDS-PAGE and silver staining of fractions obtained during purification. Four μg of total protein per lane was loaded for all unpurified samples and 1–2 μg for all pure protein fractions (α-NAGAL, α-NAGALEL, and α-GAL). Shown are: starting material/Lysate (L), bound protein to Concanavalin A (C), pooled collected eluate of ion exchange (I), and the final pooled gel filtration fraction (GL) with highest enzyme specific activity. For comparison is shown recombinant α-galactosidase A, Fabrazyme (Fz). Black asterisk indicating the α-NAGALs and red asterisk the α-GAL. (B) Before electrophoresis, 1 μg of each pure enzyme was treated with 0.25 μM of Cy5 α-galactosidase activity based probe, ABP. NEL = α-NAGALEL, N = α-NAGAL, A = α-GAL. The gels were scanned λaexc = 635 nm, then immunoblotted with anti-α-GAL or anti-NAGAL rabbit polyclonal antibodies, following Coomassie Brilliant blue, CBB, staining of the blots. The same gel had to be repeated since anti-α-GAL and anti-NAGA antibodies were both polyclonal anti-rabbit.
