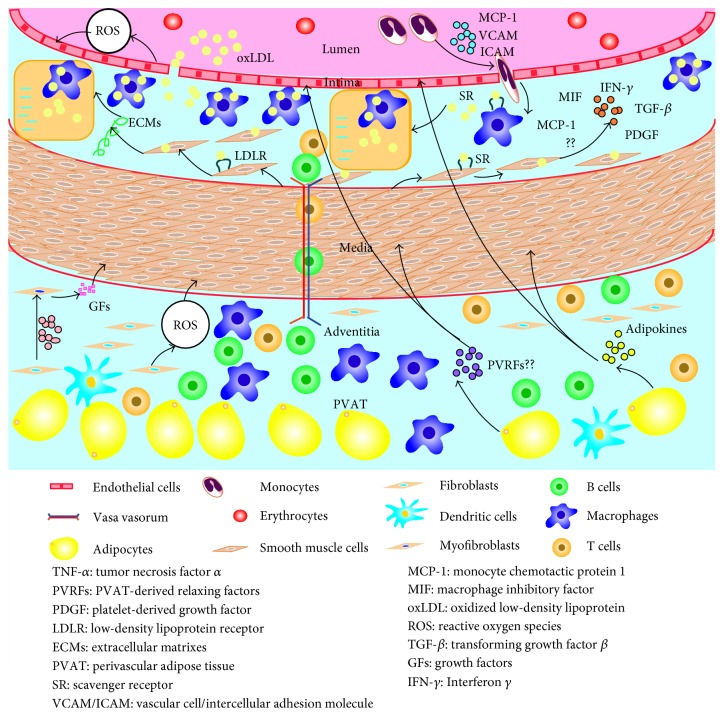
Figure 1.
Roles of different cells from the arterial vessel wall in atherosclerosis. Different cells, including endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, and adipocytes from the tunica intima, media, adventitia, and perivascular adipose tissue and their related cytokines all participate in the inflammatory response of atherosclerosis via multiple intricate pathways. Endothelial dysfunction, smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation, the transformation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, and adipokines produced by perivascular adipose tissue are predominantly implicated in the pathological process of atherosclerosis.