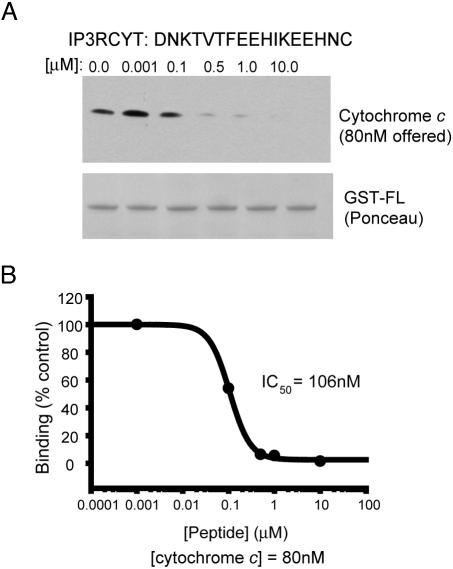
Fig. 2.
A 17-aa IP3R peptide displaces cytochrome c from IP3R. (A) A peptide encompassing the minimal cytochrome c binding domain (amino acids 2621-2636) with a C-terminal cysteine (IP3RCYT) was tested for the ability to disrupt cytochrome c/IP3R binding. Cytochrome c (80 nM) was incubated with 100 nM GST-FL and varying concentrations of IP3RCYT. Complexes were immobilized on GST-Sepharose and analyzed for cytochrome c binding by Western blotting. A Ponceau stain of the nitrocellulose blot is shown to illustrate equal loading of GST-FL. (B) Densitometric analysis of cytochrome c pull-down and subsequent graphing of percent binding (vs. no peptide) demonstrates an IC50 value of 106 nM for IP3RCYT. Data were fit to the monophasic Hill equation y = min + (max-min)/1 + (x/IC50)Hillslope. The experiment was repeated three times with essentially identical results.