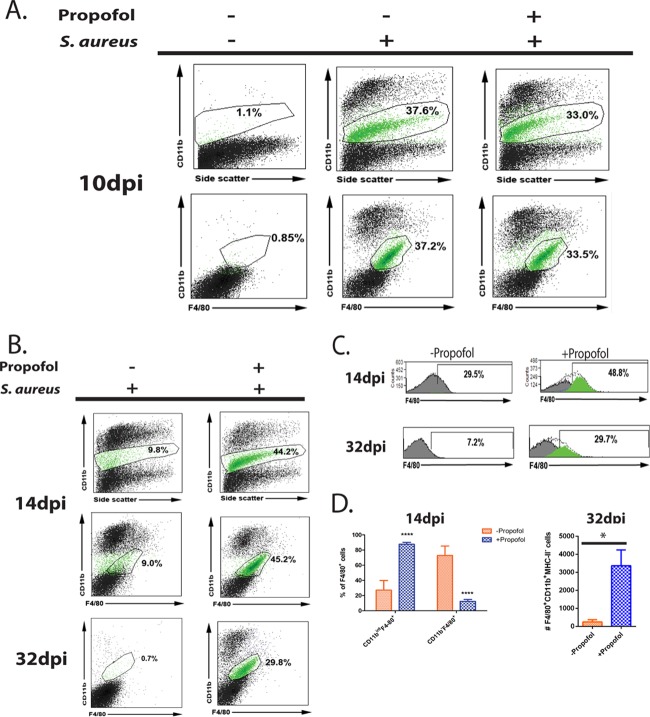
FIG 4.
Propofol treatment inhibits differentiation of monocytes into macrophages. (A) Animals were infected with 3 × 106 CFU of S. aureus via tail vein in the presence or absence of propofol. Mice were sacrificed at 10 days postinfection, and kidneys were isolated and processed for FACS analysis. While kidneys from naive mice contained negligible numbers of immune cells expressing the integrin CD11b or the macrophage marker F4/80 (left two images), kidneys from both propofol-treated mice (right two images) and infected controls (middle two images) contained similarly large numbers of CD11bint F4/80+ cells (green cell populations). (B) Animals were infected as described for panel A and sacrificed at 14 days postinfection. Kidneys were isolated and processed for FACS analysis. While kidneys from infected animals not given propofol showed a marked decrease in the CD11bint F4/80+ cell population (in green; top and middle left), kidneys from propofol-treated mice showed no significant change in this cell population from 10 days postinfection (top and middle right). This phenotype persisted up to 32 days postinfection, when kidneys from infected controls contained few CD11bint F4/80+ cells (bottom left), while those from anesthetized mice contained significant numbers (bottom right). (C) Control animals displayed significant numbers of F4/80+ cells that have lost CD11b cell surface expression at 14 days postinfection (top left). In contrast, kidneys from propofol-treated mice contained mostly CD11bint F4/80+ monocyte populations (top right). At 32 days postinfection, control animals exhibited far fewer F4/80+ cells in the kidney, whereas CD11bint F4/80+ cells persisted in significant numbers in kidneys from anesthetized mice. (D) Kidneys from propofol-treated animals contained significantly larger numbers of CD11bint F4/80+ monocytes than infected controls at 14 days postinfection. Conversely, control animals displayed considerably more F4/80+ macrophages than anesthetized mice at this same time point (top). At 32 days postinfection, propofol-treated mice contained substantial numbers of immature CD11bint F4/80+ MHC-II− monocytes in the kidney, whereas control animals had negligible numbers of this cell type. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments with 4 to 5 animals per treatment group per time point. *, P < 0.05; ****, P < 0.0001.