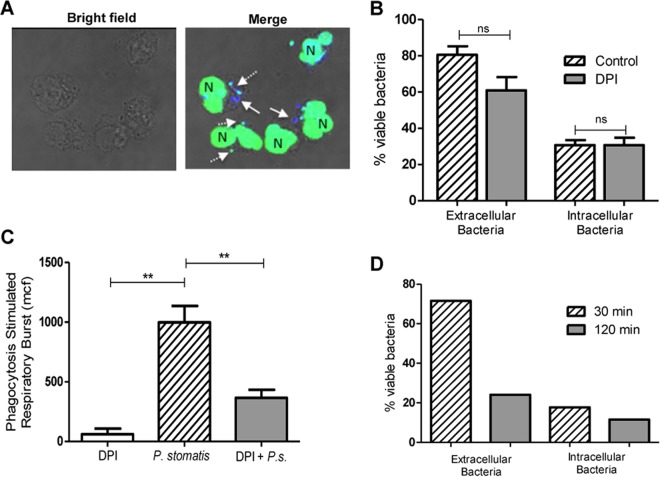
FIG 4.
Killing of P. stomatis is ROS independent. Neutrophils were challenged with P. stomatis (30 min) in the presence or absence of DPI (10 μM). (A) Representative confocal image of viable (blue) and nonviable (green/turquoise) P. stomatis strains, which were distinguished by using the BacLight viability dyes DAPI and Sytox Green. White arrows indicate viable intracellular bacteria; the dashed white arrows indicate dead intracellular bacteria. N, neutrophil nucleus. (B) Percentage of viable extracellular (external) and intracellular (internal) bacteria from 200 neutrophils with and without DPI from 3 independent experiments. ns, nonsignificant. (C) Neutrophils were challenged with P. stomatis (30 min), with P. stomatis + DPI (P.s. + DPI), or with DPI alone. Intracellular ROS production was measured by flow cytometry as described above. Data are expressed as means ± SEM of the mean channel of fluorescence (mcf) from 3 independent experiments. **, P < 0.001. (D) CGD patient neutrophils were challenged with DAPI-labeled P. stomatis for 30 or 120 min, and bacterial viability was determined using the BacLight assay. The percentage of viable extracellular (external) and intracellular (internal) bacteria from 200 CGD neutrophils was determined for each time point.